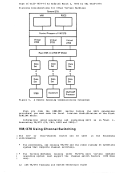
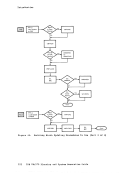
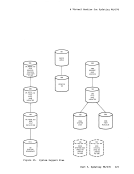
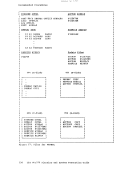
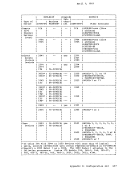
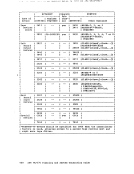
2. The maximum sizes (in cylinders) of CMS minidisks are as follows: 3330 Model 1 3330 Model 11 3340 Model 35 3340 Model 70/3344 3350 Series 203 246
492
349
682
115200 404 808 349
698
555
3.CMS employs the spooling facilities of VM/370 to perform unit
recordI/O. However, a program running under CMS can issue its own SIOs to attached dedicated unit record devices.
4.Only those as and DOS facilities that are simulated by CMS can be
used to execute as andDOS programs produced by language processors
undereMS. 5. Many types of object programs produced by CMS (and OS) languages
can be executed undereMS using CMS's simulation of as supervisory
functions. Although supported in as and.DOS virtual machines under VM/370, the writing and updating of non-VSAM OS data sets and DOS files are not supported under eMS. 6. CMS can read sequential and partitioned as data sets and sequential DOS files, by simulating certain as macros.
The following restrictions apply whenCMS reads as data sets that
reside on as disks:• Read-password-protected data sets are not read unless they are VSAM data sets. • BDAM and ISAM data sets are not read. • Multivolume data sets are
End-of-volume is treated
end-of-volume switching.
read as single-volume data
as end-of-file and there
sets.
is no• Keys in data sets with keys are ignored and only the data is
read, except forVSAM. • User labels in user-labeled data sets are bypassed.
The following restrictions apply wheneMS reads DOS files that
reside onDOS disks: • Only DOS sequential files can be read. CMS options and operands
that do not apply to as sequential data sets (such as theMEMBER and CONCAT options of FILEDEF and the PDS option of MOVEFILE) also do not apply to DOS sequential files. • The following types of DOS files cannot be read: --DOS DAM and ISAM files.
--Files with the input security indicator on.--DOS files that contain more than 16 extents. 1!Qte: User labels occupy the first extent; therefore, the file can hold
only 15 additional data extents.}
Appendix F:V8/370 Restrictions 439
492
349
682
115
698
555
3.
record
4.
used to execute as and
under
can be executed under
functions. Although supported in as and
The following restrictions apply when
reside on as disks:
End-of-volume is treated
end-of-volume switching.
read as single-volume data
as end-of-file and there
sets.
is no
read, except for
The following restrictions apply when
reside on
that do not apply to as sequential data sets (such as the
--Files with the input security indicator on.
only 15 additional data extents.}
Appendix F: