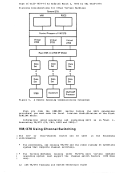
Updating RSCS Updating RSCS The same procedure used to update CP and CMS can be used to update RSCS. However, unlike CP and CKS, RSCS can test the system that is built; it
does not need to test a duplicate copy of the system that is built.
Again, theKAINT virtual machine can be used to do the updating. You should link to the RSCS virtual machine's 191 minidisk as your 195 and
access it as your A-disk.
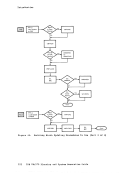
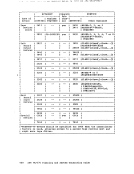
The order of search for updating is:
195A R/i 194 B/A RIO 190 S R/O To build a new RSCS nucleus, you must create a new RSCS system disk
and generate a newRSCS nucleus.
Creating anRSCS System Disk Use the following procedure to create a new RSCS system disk:
1. tog on asKAINT. 2. IPt 190. 3. tink to the mini disk that you want to contain the new RSCS nucleus
as lq5 in write status and access it as your A-disk.
4. Issue theCMS FORKAT command to format that minidisk.
5.Issue the eMS command with the RECOMP option to format the same minidisk with one or two cylinders less than the total number
of cylinders on the disk (one less on a3330 or 3350, two less on a
2314 or3340). The last cylinders are used for the RSCS nucleus.
6. If you wish to change theRSCS configuration, re-create the AXSLINKS, tAXLINES, and TAGQUEUE COpy files and create a new DKTLOC macro library. See "Part 3. Generating VM/370 (CP, CMS, RSCS and IPCS) .n 1. Generate a new RSCS nucleus using the commands described in the
following section.
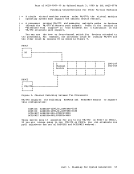
Generating theRSCS Nucleus 1. Load the RSCS files onto the CP system disk (the 194 minidisk
belonging toKAINT) if they are not already there.
2. Access theKAINT 194 disk as an extension of the RSCS system disk.
access 194 b/aPart 5. Updating VM/370 363
does not need to test a duplicate copy of the system that is built.
Again, the
access it as your A-disk.
The order of search for updating is:
195
and generate a new
Creating an
1. tog on as
as lq5 in write status and access it as your A-disk.
4. Issue the
5.
of cylinders on the disk (one less on a
2314 or
6. If you wish to change the
following section.
Generating the
belonging to
2. Access the
access 194 b/a