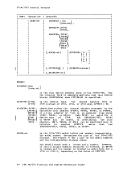
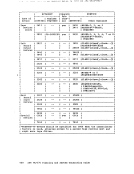
Minidisks
Minidisks
The external storage requirements of multiple virtual machines executing
concurrently would be excessive if each virtual machine were assigned
one real direct access storage device for each virtual DASD specified in
its configuration.
Therefore, if you do not require the full capacity of a real DASD,
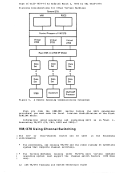
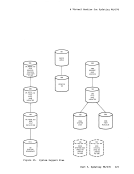
you can be assigned one or more minidisks instead. A minidisk is a
logical subdivision of a physical disk pack with its own virtual device
address, virtual cylinders (starting with0, 1, 2, and so on) and a VTOC
(volume table of contents or disk label identifier). Each of your
minidisks is preallocated the number of contiguous full cylinders that
were specified in theVM/370 MDISK directory record, and that space is
considered to be a complete virtual disk device.
Minidisks are controlled and managed byCPa If a virtual machine
attempts to use DASD space beyond the boundaries defined for its
minidisks,CP presents a command reject (seek check) to the virtual
machine. If a system is to be run on both a virtual and a real machine,
minidisks for that system must start at real cylinder zero. For a
detailed list of minidisk restrictions, see "Appendix F:V"/370 Restrict ions. " The remainder of this section describes the following characteristics
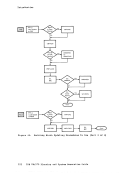
of minid isks:• Definition • Space allocation • Track characteristics • Alternate tracks • Labels
O f"" M" "d" k9_lnlng Inl IS S Permanent minidisks are defined in the VM/370 directory entry for a
virtual machine. A minidisk defined in the directory via an"DISK statement is a permanent part of the virtual machine configuration and
the data on the minidisk is available to the user from session to
session.
If any virtual machine has a temporary requirement for direct access
space, this can be filled from a pool of T-disk space.You specify the
size of the T-disk pool when you allocate disk space with the standalone
Format/Allocate program. Minidisks created from the T-disk area must be
initialized and are available to the virtual machine for the duration of
one terminal session.When the virtual machine logs off or issues a CP command to release the temporary minidisk, the area is returned to CPa It is up to you to allocate minidisks on V"/370 disks in a manner
that minimizes arm contention and physical overlap. Information about
minimizing arm contention is found in the"Preparing the CP System Control File Part 2. V"/370 directory function neither checks nor flags overlapped
or duplicate minidisk extents. Nor does the function provide DASD space
records for unused space or used space.Part 1. Planning for System Generation 95
Minidisks
The external storage requirements of multiple virtual machines executing
concurrently would be excessive if each virtual machine were assigned
one real direct access storage device for each virtual DASD specified in
its configuration.
Therefore, if you do not require the full capacity of a real DASD,
you can be assigned one or more minidisks instead. A minidisk is a
logical subdivision of a physical disk pack with its own virtual device
address, virtual cylinders (starting with
(volume table of contents or disk label identifier). Each of your
minidisks is preallocated the number of contiguous full cylinders that
were specified in the
considered to be a complete virtual disk device.
Minidisks are controlled and managed by
attempts to use DASD space beyond the boundaries defined for its
minidisks,
machine. If a system is to be run on both a virtual and a real machine,
minidisks for that system must start at real cylinder zero. For a
detailed list of minidisk restrictions, see "Appendix F:
of minid isks:
O f"" M" "d" k
virtual machine. A minidisk defined in the directory via an
the data on the minidisk is available to the user from session to
session.
If any virtual machine has a temporary requirement for direct access
space, this can be filled from a pool of T-disk space.
size of the T-disk pool when you allocate disk space with the standalone
Format/Allocate program. Minidisks created from the T-disk area must be
initialized and are available to the virtual machine for the duration of
one terminal session.
that minimizes arm contention and physical overlap. Information about
minimizing arm contention is found in the
or duplicate minidisk extents. Nor does the function provide DASD space
records for unused space or used space.