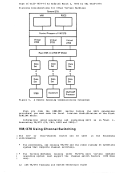
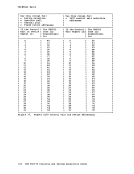
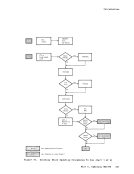
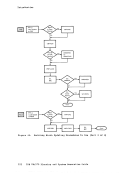
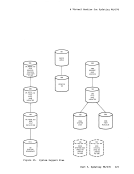
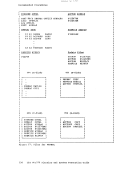
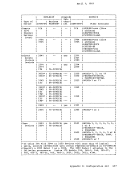
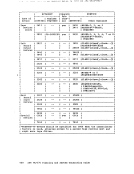
Directory Program ISAM channels. If a virtual machine with the
executes in basic control mode, theI/O masking for channels 6
and higher is simulated by the extended channel feature. If a
virtual machine with theEC"ODE option executes in extended
control mode, theI/O masking for all 16 channels is handled
via extended control register 2. This facility can also be
obtained by issuing theCP command SET EC"ODE ON. provides special channel command word translation routines
that permitas/pcP, "FT, and MVT ISA" programs (which
dynamically modify theirCCis) to operate properly in a
virtual machine. This is required only for virtual machines
that useas/pcP, MVT ISAM access methods or OS/VS ISA" when executing in a V=R partition under OS/VS. This option is
not needed forDOS, DOS/VS, or OS/VS ISAM when run only in a V=V partition of OS/VS. This facility can also be obtained by
issuing theCP command SET ISAM ON. VIRT=REAL is a performance option that allows the user to place his
virtual machine in lowerstorage. such that its virtual
storage addresses correspond to the real storage address
(except for its page zero, which is relocated). The real pageACCT SVCOFF zero is controlled by the CP nucleus. No CCi translation is
required. This option is required for a virtual machine to
successfully execute self-modifying channel programs other
than those generated byOS/VS TCAM (Level 5, generated or
invoked with theVM/370 option) or OS ISAM. VIRT=REAL can be
specified for any number of virtual machines but only one
virtual machine can use this facility at any given time. A
named or sharedsystem cannot be loaded (via IPL) in a
virtual=real area. The device address must be specified in
theIPL command. To generate a VM/370 system with a
virtual=real machine, see"Specifying a Virtual=Real Machine" in the Part 1.
a user with theACCT option in his directory can charge
another user for virtual machine resources. For example, a
user who sends a job to theCftS batch virtual machine can be
charged for the time that he uses in the batch machine. Note
that theACCT option should be specified in the directory of
theCftSBATCH virtual machine so that user/job identifying
information will be printed on the forms separator that
separates spooled output files.
specifies thatCP, instead of the virtual machine assist
feature or theV"/370 Extended Control - Program Support handles all SVC interrupts for this virtual machine. A user
whose directory entry contains this option can override it by
issuingSET ASSIST SVC. SVC 76 interrupts are handled by CP whether or not
theSVCOFF option is specified. BftX specifies that all virtual machine I/O operations are to occur
as block multiplexer channel operations rather than selector
channel (the default) operations. In block multiplexermode, the virtual channel is not busy until the initial 510 is
complete (selector mode operates similarly). Block
multiplexer allows the successful start of multipleSIOs to
different devices on the same channel. However, virtualI/O operations on channel 0 are processed as byte multiplexer
channel operations.Channels that have a channel-to-channel
adapter are restricted to selector channel operation.204 IBft VM/370 Planning and System Generation Guide
executes in basic control mode, the
and higher is simulated by the extended channel feature. If a
virtual machine with the
control mode, the
via extended control register 2. This facility can also be
obtained by issuing the
that permit
dynamically modify their
virtual machine. This is required only for virtual machines
that use
not needed for
issuing the
virtual machine in lower
storage addresses correspond to the real storage address
(except for its page zero, which is relocated). The real page
required. This option is required for a virtual machine to
successfully execute self-modifying channel programs other
than those generated by
invoked with the
specified for any number of virtual machines but only one
virtual machine can use this facility at any given time. A
named or shared
virtual=real area. The device address must be specified in
the
virtual=real machine, see
a user with the
another user for virtual machine resources. For example, a
user who sends a job to the
charged for the time that he uses in the batch machine. Note
that the
the
information will be printed on the forms separator that
separates spooled output files.
specifies that
feature or the
whose directory entry contains this option can override it by
issuing
the
as block multiplexer channel operations rather than selector
channel (the default) operations. In block multiplexer
complete (selector mode operates similarly). Block
multiplexer allows the successful start of multiple
different devices on the same channel. However, virtual
channel operations.
adapter are restricted to selector channel operation.