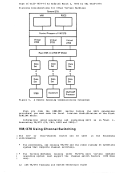
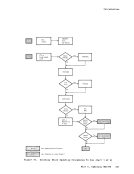
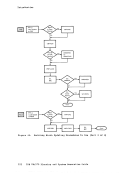
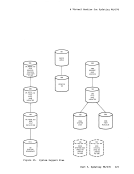
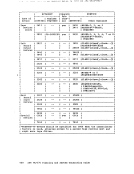
Installation Verification Procedure Verifying CP and CMS Using the IVP The Installation Verification Procedure (IVP) for VM/370 exercises CP and CMS to verify that they are working properly. The IVP is contained
in two files using theEXEC facility of CMS, and uses two virtual
machines in addition to the system operator's virtual machine.
The tests exercise the following areas ofCP: Multiple virtual machine support I/O spooling
Transferring of spooled data to other virtual machinesOffline I/O operations
Sending of messages to the system operatorPaging operations
Task dispatching and scheduling
DiskI/O support
Automatic warm start following abnormal termination ofVM/370 Verifying that the correct EC level is on machines with
Extended Control-program Support
The following facilities ofCMS are exercised:
NormalCMS command processing
Disk formatting
Copying of files
Creation and modification of files via EDIT command
Assembly of executable programs
Execution of user programs
Creation and execution of user-written commandsPrinting and punching of CMS files
Issuing of commands toCP Use of multilevel nested EXEC procedures
Stacking and unstacking of command and data input from the terminal
Communicationwith user from EXEC procedures Several other system facilities, incidental to the primary rvp tests, are exercised. Certain system facilities such as preferred execution
options, virtual=real, asISAM, and RSCS (Remote Spooling Communications
Subsystem) are not exercised by theIVP. The IVP requires operator
intervention only when an operational decision is to be made, or to
initiate theIVP tests themselves. All file creation, erasure,
management, and logoff of the virtual machines (with the exception of
the system operator) at test completion is performed without operator or
user action.
TheIVP tests use only the system-provided facilities. All unique
test programs are created, assembled, and subsequently erased by thelVP. Facilities Required for Each IVP Virtual Machine
AllVM/370 configurations are supported. The lVP executes under the
control ofCMS. The other facilities required are: • The assembler • One virtual read/write disk accessed as the A-disk (usually 191) • 320K of virtual storage (16M for IVPM1) Part 3. Generating VM/370 (CP, CMS, RSCS, and lPCS) 263
in two files using the
machines in addition to the system operator's virtual machine.
The tests exercise the following areas of
Transferring of spooled data to other virtual machines
Sending of messages to the system operator
Task dispatching and scheduling
Disk
Automatic warm start following abnormal termination of
Extended Control-program Support
The following facilities of
Normal
Disk formatting
Copying of files
Creation and modification of files via EDIT command
Assembly of executable programs
Execution of user programs
Creation and execution of user-written commands
Issuing of commands to
Stacking and unstacking of command and data input from the terminal
Communication
options, virtual=real, as
Subsystem) are not exercised by the
intervention only when an operational decision is to be made, or to
initiate the
management, and logoff of the virtual machines (with the exception of
the system operator) at test completion is performed without operator or
user action.
The
test programs are created, assembled, and subsequently erased by the
All
control of