FILEDEF 1/0 must not be blocked). PRINTER is the spooled printer. PUNCH is the spooled punch. 1/0 must not be
blocked)• DISK specifies that the virtual 1/0 device is a disk.
the format, you can choose one of two forms for specifying theDISK operand. Both forms are described in "Using the FILEDEF DISK Operand." DUMMY indicates that no real 1/0 takes place for a data set.
can be 1, 2, 3, or 4, representing virtual units 181, 182,
183, and 184, respectively. If n is not specified, FILEDEF
uses the existingTAPn device for the specified ddname. TAPn defaults to
specified ddname, or if the existing device was notTAPn.
Clearing a ddname before defining it ensures that a file
definition does not exist and that any options previously
defined with the ddname no longer have effect.
rWhenever an invalid option is specified for a particular
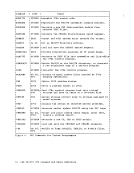
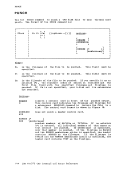
device type, an error message is issued. Figure 8 shows valid
options for each device type.I , options PUNCH, DISK , PRINTER , TERMINAL TAPn BLOC.K, BLKSIZE t X X CHANGE, NOCHANGE t X X CONCAT DEN 1 DISP MOD X KEYLEN LIMCT LOWCASE, UPCASE 1 LRECL X X X MEMBER OPTCD PERM X X X RECFM X X 1 TRTCH X3 tTENT 7'!'RACK, X lNo options may be necessary but all disk options are accepted.
2This option isBDAM files.
3This option is for 7-track tapes only.DUKMYl 1 1 1 X X 12 12 1 1 12 X X 12 L- J
Each Device Type of the Figureq. Valid File Characteristics for
FILEDEF Command90 IBM VM/370 CMS Command and Macro Reference
blocked)
the format, you can choose one of two forms for specifying the
can be 1, 2, 3, or 4, representing virtual units 181, 182,
183, and 184, respectively. If n is not specified, FILEDEF
uses the existing
specified ddname, or if the existing device was not
Clearing a ddname before defining it ensures that a file
definition does not exist and that any options previously
defined with the ddname no longer have effect.
r
device type, an error message is issued. Figure 8 shows valid
options for each device type.
2This option is
3This option is for 7-track tapes only.
Each Device Type of the Figure
FILEDEF Command