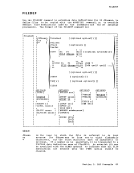
FILEDEF OPTCD a is the direct access search processing desired. The
variable "a" may be any combination of up to three of the
following: (A and R are mutually exclusive.)A E
F
R
DASD Search
Extended search
Feedbackaddressinq Relative block addressing
Note: TheKEYlEN, tTENT, LIMCT, and OPTCD options should only be used with BDAM files. DISP MOD positions the read/write pointer after the last record in
the disk file. This option should only be used for
output files.MEMBER membername CONCAT DSORG un r ,
allowsyou to specify the name of a member
partitioned data set; membername is the name
member.
of anOS of the PDS allows you to assign the same ddname to two or more OS macro libraries so that you can refer to them in a single GLOBAL command.
Any file format options you specify in the first FILEDEF
command line remain in effect for subsequently
concatenated libraries. For a detailed description of
concatenated macro libraries, see"Using OS Macro libraries" in VML170 CM§. 2yidg ..
is the data set organization: physical sequentialCPS), partitioned (PO), or direct access CDA). , 1TRACK, is the tape setting. , qTRACK I L J
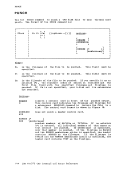
TRTCR a is the tape recording technique for 7-track tapes.Use the following chart to determine the value of "a" for
7-track tapes.
DEN denLOWCASE r0- t I a Parit y Converter Translator I I I , 0 odd off off , , OC odd on off I , OT odd off on I , E even off off I I ET even off on , L-- J 200, 556, 800, 1600, or 6250 bpi (bits per inch). If 200 or 556 are specified, 7TRACK
is assumed. If800, 1600, or 6250 are specified 9TRACK is
assumed.
translates all terminal input data touppercase. retains all terminal input data as typed in. 92 IBM VM/370 CMS Command and Macro Reference
variable "a" may be any combination of up to three of the
following: (A and R are mutually exclusive.)
F
R
DASD Search
Extended search
Feedback
Note: The
the disk file. This option should only be used for
output files.
allows
partitioned data set; membername is the name
member.
of an
Any file format options you specify in the first FILEDEF
command line remain in effect for subsequently
concatenated libraries. For a detailed description of
concatenated macro libraries, see
is the data set organization: physical sequential
TRTCR a is the tape recording technique for 7-track tapes.
7-track tapes.
DEN den
is assumed. If
assumed.
translates all terminal input data to