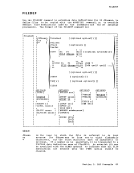
FILEDEF
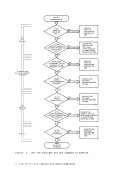
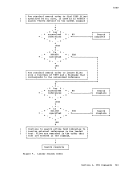
6. If a FILEDEF commandis issued with a
the same, the filename, filetype, fi1emode, and options previously
specified remainin effect, unless respecified by the new FILEDEF
command. If the devices are not the same, all previous
specifications are removed.
7. If the FILEDEF command is enteredwith no operands
r a list of
current1efinitions is displayed.
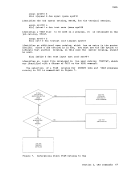
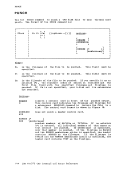
There are two general forms forspecifying the DISK operand in a FILEDEF
command. If you specify the first form:
FILEDEF ddname DISK fn ft (fm]
fn and ft (filename and filetype) are assumed to be aCKS fi1eid. If fm is the filemode of an as disk, fn and ft are assumed to be the only two
qualifiers of an as data set name. If fmis specified as an asterisk,
(*) then all disks are searched until a file with matching fn and ft is
found.You cannot use this form unless the OS data set name or DOS file-id
conforms to the as naming convention (1-to a-byte
by periods, to a maximum of 44 characters, including periods). Also,
the data set name can have only two qualifiers; otherwise, you must use
the DSN ? or DSN qua1l••• form. For example, if the OS data set name
orDOS fi1e-id is TEST.SAMPLE.MAY, you enter:
FILEDEFMINE Bl DSN TEST SAMPLE MAY -- or --
FILEDEFKINE Bl DSN ?
TEST.SAMPLE. MAY If the OS data set name or DOS fi1e-id is TEST.SAMPLE, then you may
enter:
FILEDEFKINE DISK TEST SAMPLE B1
The second form of the DISK operandis used only with OS data sets
andDOS files: r , .. ,
FILEDEF ddnameIDISK fn ft I Ifml {DSN ? } I IAll DSN qua1l [qua12 ••• ]
L .J L.J This form allows you to to enter OS and DOS file identifications that do not conform to as data set naming conventions. The DSN operand
corresponds to the DSN parameter on theOS DD (data definition)
statement. There are three ways you can specify this form:• FILEDEF ddname DISK fn ft fm DSN qua1l (qua12 ••• ]
This form of the FILEDEF command associates theCKS filename and
filetype you specify with the as data set name orDOS file-id specified
following theDSN operand. Once it is defined, you can refer to the OS data set name or DOS fi1e-id by using the eMS filename and filetype. If
you omit DISK, filename, filetype, and filemode, the d9fau1t values are
FILE ddname Al.
94IBK CMS Command and Macro Reference
6. If a FILEDEF command
the same, the filename, filetype, fi1emode, and options previously
specified remain
command. If the devices are not the same, all previous
specifications are removed.
7. If the FILEDEF command is entered
r a list of
current
There are two general forms for
command. If you specify the first form:
FILEDEF ddname DISK fn ft (fm]
fn and ft (filename and filetype) are assumed to be a
qualifiers of an as data set name. If fm
(*) then all disks are searched until a file with matching fn and ft is
found.
conforms to the as naming convention (1-to a-byte
by periods, to a maximum of 44 characters, including periods). Also,
the data set name can have only two qualifiers; otherwise, you must use
the DSN ? or DSN qua1l
or
FILEDEF
FILEDEF
TEST.
enter:
FILEDEF
The second form of the DISK operand
and
FILEDEF ddname
L .J L
corresponds to the DSN parameter on the
statement. There are three ways you can specify this form:
This form of the FILEDEF command associates the
filetype you specify with the as data set name or
following the
you omit DISK, filename, filetype, and filemode, the d9fau1t values are
FILE ddname Al.
94