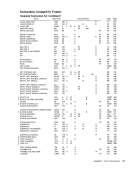
Condition Channel control check
Status stored bySTART I/O or START I/O FAST RELEASE
Status stored by HALTI/O or HALT DEVICE Program check
Protection check
Chaining check
Termination under countcontrol Termination by I/O device
Termination by HALTI/O or HALT DEVICE Termination by CLEAR I/O Suppression of command chaining due to unit check or unit
exception with device end orcontrol unit end
Termination on command chaining by busy, unit check,
or unit exception
Deferred Gondition code 1 or 3 forSTART I/O FAST RELEASE PCI flag in CCW Interface control check Channel end after HALT I/O on selector channel Channel end after CLEAR I/O Control unit end
Device end
Attention
Busy
Statusmodifier Contents of the CSW Count Field
contents of the CCW causes the command to be
rejected during execution of STARTI/O or START I/O FAST RELEASE, the CSW stored by the in
struction mayor may not contain thePCI bit. Fur
thermore, when the channel detects a programming
error in the CAW or in the first CCW, thePCI bit
may unpredictably appear in a CSW stored by
STARTI/O or START I/O FAST RELEASE with
out thePCI flag being on in the first CCW associat
edwith the instruction.
ing contains thePCI flag but an unusual condition
signaled by the device precludes the initiation of the
operation, thePCI bit appears in the CSW associat
ed with the interruption condition. Likewise, if de
vice status causes the command to be rejected during
execution of STARTI/O or START I/O FAST
RELEASE, the CSW stored by the instruction con
tains thePCI bit.
Conditions detected by the channel are not relat
ed to those identified by theI/O device.
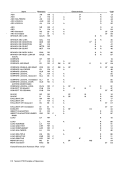
The following table summarizes the handling of
status bits. The table lists the states and activities
that can cause status indications to be created and
the methods by which these indications can be
placed in the CSW.
238System/370 Principles of Operation Contents of Field Unpredictable
Unchanged
Unchanged
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
Correct
Correct
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
Correct. Residual count oflast CCW used in the completed
operation.
Correct.Original count of CCW specifying the new operation.
Correct.Original count of CCW specifying the new operation.
Unpredictable
UnpredictableZero Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero Channel Logout
When a channel stores a CSW that indicates the
channel-control-check condition in the absence of
the logout-pending indication, or the interface
control-check condition, or, on some channels, the
channel-data-check condition, a channel logout,
useful for error-recovery or diagnostic purposes,
accompanies the storing of the CSW. The logout
may be a limited channel logout, a full channel log
out, or both. The type of logout that occurs and, for
the full logout, the length of the logout and the loca
tion at which it is stored, depend on the channel type
and model number.
The limited channel logout contains model
independent information and is stored at realloca
tions 176-179 of theCPU to which the channel is
configured. When it is stored, bit0 of the logout is
always stored as a zero.
The full channel logout contains model-dependent
information. When the length of the full channel
logout exceeds 96 bytes, it is stored at the location
specified by theI/O extended logout (IOEL) point
er in reallocations 173-175 of theCPU to which the
channel is configured. When the length of the full
channel logout is 96 bytes or fewer, the channel may
either use the10EL pointer or may store the logout
in the fixed-logout area, reallocations 256-351 of
Status stored by
Status stored by HALT
Protection check
Chaining check
Termination under count
Termination by HALT
exception with device end or
Termination on command chaining by busy, unit check,
or unit exception
Deferred Gondition code 1 or 3 for
Device end
Attention
Busy
Status
contents of the CCW causes the command to be
rejected during execution of START
struction mayor may not contain the
thermore, when the channel detects a programming
error in the CAW or in the first CCW, the
may unpredictably appear in a CSW stored by
START
out the
ed
ing contains the
signaled by the device precludes the initiation of the
operation, the
ed with the interruption condition. Likewise, if de
vice status causes the command to be rejected during
execution of START
RELEASE, the CSW stored by the instruction con
tains the
Conditions detected by the channel are not relat
ed to those identified by the
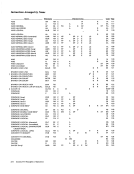
The following table summarizes the handling of
status bits. The table lists the states and activities
that can cause status indications to be created and
the methods by which these indications can be
placed in the CSW.
238
Unchanged
Unchanged
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
Correct
Correct
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
Correct. Residual count of
operation.
Correct.
Correct.
Unpredictable
Unpredictable
When a channel stores a CSW that indicates the
channel-control-check condition in the absence of
the logout-pending indication, or the interface
control-check condition, or, on some channels, the
channel-data-check condition, a channel logout,
useful for error-recovery or diagnostic purposes,
accompanies the storing of the CSW. The logout
may be a limited channel logout, a full channel log
out, or both. The type of logout that occurs and, for
the full logout, the length of the logout and the loca
tion at which it is stored, depend on the channel type
and model number.
The limited channel logout contains model
independent information and is stored at realloca
tions 176-179 of the
configured. When it is stored, bit
always stored as a zero.
The full channel logout contains model-dependent
information. When the length of the full channel
logout exceeds 96 bytes, it is stored at the location
specified by the
er in reallocations 173-175 of the
channel is configured. When the length of the full
channel logout is 96 bytes or fewer, the channel may
either use the
in the fixed-logout area, reallocations 256-351 of