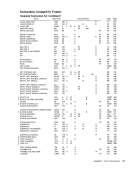
Appendix H. EBCDIC Chart
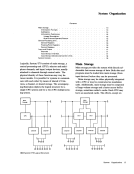
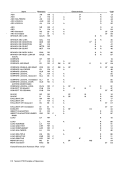
Extended Binary-Coded-Decimallnterchange Code(EBCDIC) The 256-position EBCDIC table, outlined by the heavy
black lines, shows the graphic characters and controlchar acter representations for EBCDIC. The bit-position numbers,
bit patterns, hexadecimal representations and card hole
patterns for these and other possibleEBCDIC characters are
also shown.
To find the card hole patterns for most characters, parti
tion the 256-position table into four blocks as follows:
1
3
2
4
Block 1: Zone punches at top of table;
digit punches at left
Block 2: Zone punches at bottom of table;
digit punches at left
Block 3: Zone punches at top of table;
digit punches at right
Block 4 : Zone punches at bottom of table;
digit punches at right
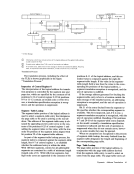
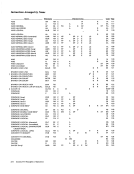
Fifteen positions in the table are exceptions to the above
arrangement. These positions are indicated by smallnum bers in the upper right corners of their boxes in the table.
The card hole patterns for these positions are given at the
bottom of the table. Bit-position numbers, bit patterns, and
hexadecimal representations for these positions are fouri.d in
the usual manner.
Following are some examples of the use of theEBCDIC chart: Character Type
PFControl Character % Special Graphic
R UpperCase a Lower ase Control Character, function not yet assigned Bit Pattern 00000100 01 101100 1101 1001 10000001 00 11 0000 -.. Bit Positions 01 234567
Hex04 6C 09 81 30 Hale Pattern
Zone Punches I Digit Punches12-9
1
-4 01- 8 - 111- 9
12 -111·- I 1 Appendix H. EBCDIC Chart 287
Extended Binary-Coded-Decimallnterchange Code
black lines, shows the graphic characters and control
bit patterns, hexadecimal representations and card hole
patterns for these and other possible
also shown.
To find the card hole patterns for most characters, parti
tion the 256-position table into four blocks as follows:
1
3
2
4
Block 1: Zone punches at top of table;
digit punches at left
Block 2: Zone punches at bottom of table;
digit punches at left
Block 3: Zone punches at top of table;
digit punches at right
Block 4 : Zone punches at bottom of table;
digit punches at right
Fifteen positions in the table are exceptions to the above
arrangement. These positions are indicated by small
The card hole patterns for these positions are given at the
bottom of the table. Bit-position numbers, bit patterns, and
hexadecimal representations for these positions are fouri.d in
the usual manner.
Following are some examples of the use of the
PF
R Upper
Hex
Zone Punches I Digit Punches
1
-4
12 -11