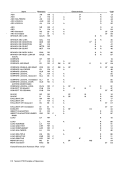
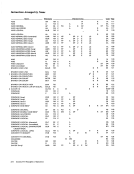
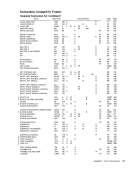
Contents DIAGNOSE. . INSERT PSW KEY INSERT STORAGE KEY LOAD CONTROL . . LOAD PSW . . LOAD REAL ADDRESS PURGE TLB.
READDIRECT. . . RESET REFERENCE BIT. SET CLOCK. . . . SET CLOCK COMPARATOR. SET CPU TIMER . . . . SET PREFIX SET PSW KEY FROM ADDRESS. SET STORAGE KEY . SET SYSTEM MASK . . SIGNAL PROCESSOR. . STORE CLOCK COMPARATOR. STORE CONTROL. . STORE CPU ADDRESS STOR E CPU ID. . STORE CPU TIMER STORE PREFIX. STORE THEN AND SYSTEM MASK STORE THEN OR SYSTEM MASK WRITE DIRECT The system-control instructions include all privileged
instructions that are described in this manual except
the input/ output instructions, which are described in
the chapter "Input/Output Operations."
The system-control instructions and their mne
monics, formats, and operation codes are listed in
the following table. The table also indicates when
the condition code is set and the exceptional condi
tions in operand designations, data, or results that
cause a program interruption.
Note: In the detailed descriptions of the individual
instructions, the mnemonic and the symbolic oper
and designation for the IBM System/370 assembly
language are shown with each instruction. ForLOAD PSW, for example, LPSW is the mnemonic
and D2(B2) the operand aesignation.
Diagnose
83
o 8 31
TheCPU performs built-in diagnostic functions, or
other model-dependent functions. The purpose of
the diagnostic functions is to verify proper function-
System-Control Instructions103 104 105 105 105 106 107 107 107 108 108 109 109 109 110 110 110 111
111
112
112
113
113
113
114
114
ing ofCPU equipment and to locate faulty compo
nents. Other model-dependent functions may in
clude disabling of failing buffers, reconfiguration of
storage and channels, and modification of control
storage.
Bits 8-31 may be used as in the SI or RS formats,
or in some other way, to specify the particular diag
nostic function. The use depends on the model.
The execution of the instruction may affect the
state of theCPU and the contents of a register or
storage location, as well as the progress of anI/O operation. Some diagnostic functions cause the test
light of the system console to be turned on.
Condition Code: The code is unpredictable.
Program Exceptions:
Privileged Operation
Depending on the model, other exceptions may be
recognized.
Programming Notes
Since the instruction is not intended for problem
program or supervisor-program use, DIAGNOSE
has no mnemonic.
DIAGNOSE, unlike other instructions, does not
System-Control Instructions103
READ
instructions that are described in this manual except
the input/ output instructions, which are described in
the chapter "Input/Output Operations."
The system-control instructions and their mne
monics, formats, and operation codes are listed in
the following table. The table also indicates when
the condition code is set and the exceptional condi
tions in operand designations, data, or results that
cause a program interruption.
Note: In the detailed descriptions of the individual
instructions, the mnemonic and the symbolic oper
and designation for the IBM System/370 assembly
language are shown with each instruction. For
and D2(B2) the operand aesignation.
Diagnose
83
o 8 31
The
other model-dependent functions. The purpose of
the diagnostic functions is to verify proper function-
System-Control Instructions
111
112
112
113
113
113
114
114
ing of
nents. Other model-dependent functions may in
clude disabling of failing buffers, reconfiguration of
storage and channels, and modification of control
storage.
Bits 8-31 may be used as in the SI or RS formats,
or in some other way, to specify the particular diag
nostic function. The use depends on the model.
The execution of the instruction may affect the
state of the
storage location, as well as the progress of an
light of the system console to be turned on.
Condition Code: The code is unpredictable.
Program Exceptions:
Privileged Operation
Depending on the model, other exceptions may be
recognized.
Programming Notes
Since the instruction is not intended for problem
program or supervisor-program use, DIAGNOSE
has no mnemonic.
DIAGNOSE, unlike other instructions, does not
System-Control Instructions