System Organization Contents
Main Storage.Information Formats
AddressingI nformation Positioning Integral Boundaries.
Byte-Oriented-Operand FeatureCentral ,Processing Unit. General Registers Floating-Point Registers Control Registers I nput and Output Channels. Input/Output Interface. Input/Output Devices and Control Units.
SystemConsole .
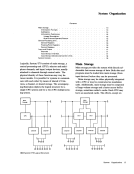
Logically,Systerri/370 consists of main storage, a
central processing unit (CPU), selector and multi
plexer channels, and input/output devices, usually
attached tochannels through control units. The
physical identity of these functions may vary be
tween models. It is possible for systems to communi
cate with each other by means of sharedI/O de
vices, a channel, or shared storage. The accompany
ing illustration depicts the logical structure for a
single-CPU system and for a two-CPU mUltiprocess
ing system.
Main
Storage
CPU
Channel Chennel
IBMSystem/370 Logical Structures
Channel
Main Storage
13
14
14
15
15
15
15
16
16
16
17
17
17
18
18
Main storage provides the system with directly ad
dressable fast-access storage of data. Both data and
programs must be loaded into main storage (from
input devices) before they can be processed.
Main storage may be either physically integrated
with aCPU or may be constructed as standalone
units. Additionally, main storage may be composed
of large-volume storage and a faster access buffer
storage, sometimes called a cache. EachCPU may
have an associated cache. The effects, except on
CPU
Channel
Main
Storage
CPU
Channel ChannelSystem Organization 13
Main Storage.
Addressing
Byte-Oriented-Operand Feature
System
Logically,
central processing unit (CPU), selector and multi
plexer channels, and input/output devices, usually
attached to
physical identity of these functions may vary be
tween models. It is possible for systems to communi
cate with each other by means of shared
vices, a channel, or shared storage. The accompany
ing illustration depicts the logical structure for a
single-CPU system and for a two-CPU mUltiprocess
ing system.
Main
Storage
CPU
Channel Chennel
IBM
Channel
Main Storage
13
14
14
15
15
15
15
16
16
16
17
17
17
18
18
Main storage provides the system with directly ad
dressable fast-access storage of data. Both data and
programs must be loaded into main storage (from
input devices) before they can be processed.
Main storage may be either physically integrated
with a
units. Additionally, main storage may be composed
of large-volume storage and a faster access buffer
storage, sometimes called a cache. Each
have an associated cache. The effects, except on
CPU
Channel
Main
Storage
CPU
Channel Channel