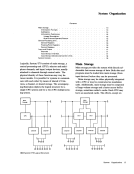
Channel Command Word
The channel command word (CCW) specifies the
command to be executed and, for commands initiat
ingI/O operations, it designates the storage area
associated with the operation and the action to be
taken whenever transfer to or from the area is com
pleted. The CCWs can be located anywhere in main
storage, and more than one can be associated with a
STARTI/O or START I/O FAST RELEASE.
The first CCW is fetched during the execution of
ST ARTI/O or START I/O FAST RELEASE being
executed as STARTI/O. When START I/O FAST
RELEASE is executed independently of the device,
the first CCW is fetched subsequent to the execution
of STARTI/O FAST RELEASE. Each additional
CCW in the sequence is obtained when the opera
tion has progressed to the point where the additional
CCW is needed. Fetching of the CCWs by the chan
nel does not affect the contents of the location in
main storage.
The CCW has the following format:
Command
Code
o 8I Flags 32 38 40 Data Address
48
31
Count
The fields in the CCW are allocated for the follow
ing purposes:C()mmand Code: Bits 0-7 specify the operation to
be performed.
63
Data Address: Bits 8-31 specify the location of an
eight-bit byte in absolute main storage. It is the first
location referred to in the area designated by the
CCW.
Chain-Data (CD) Flag: Bit 32, when one, specifies
chaining of data. It causes the storage area designat
ed by the next CCW to be used with the current
operation.
Chain-Command (CC) Flag: Bit 33, when one, and
when the CD flag is zero, specifies chaining of com
mands. It causes the operation specified by the com
mand code in the next CCW to be initiated on nor
mal completion of the current operation.
Suppress-Length-Indication (SLI) Flag: Bit 34 con
trols whether an incorrect-length condition is to be
indicated to the program. When this bit is one and
the CD flag is zero, the incorrect-length indication is
suppressed. When both the CC and SLI flags are
one, command chaining takes place regardless of the
presence of an incorrect-length condition.
Skip (SKIP) Flag: Bit 35, when one, specifies sup
pression of transfer of information to storage during
a read, read backward, or sense operation.
Program-Controlled-Interruption (PCI) Flag: Bit
36, when one, causes the channel to generate an
interruption condition when the CCW takes control
of the channel. When bit 36 is zero, normal opera
tion takes place.
Indirect DataAddress (IDA) Flag: Bit 37, when
one, specifies indirect data addressing. (The flag is
valid in both BC and EC modes.)
Count: Bits 48-63 specify the number of eight-bit
byte locations in the storage area designated by the
CCW.
Bit positions 38-39 of every CCW other than one
specifying transfer in channel must contain zeros.
Additionally, if indirect addressing is specified, bits30-31 of the CCW must be zeros, indicating a word
boundary, and bits0-7 of the first entry of the indi
rect data address list must be zeros. (See "Channel
Indirect Data Addressing.")Otherwise, a program
check condition is generated. When the first CCW
designated by the CAW does not contain the re
quired zeros, theI/O operation is not initiated, and
the status portion of the CSW with the program
check indication is stored during execution of
ST ARTI/O or, if being executed as START I/O, ST ART I/O FAST RELEASE. Detection of this
condition during data chaining causes theI/O device
to be signaled to conclude the operation. When the
absence of these zeros is detected during command
chaining or subsequent to the execution of STARTI/O FAST RELEASE, the new operation is not
initiated, and an interruption condition is generated.
The contents of bit positions40-47 of the CCW
are ignored.
Programming Note
Bit positions 38-39 of the CCW, which presently
must contain zeros, may in the future be assigned for
the control of new functions. It is therefore recom
mended that these bit positions not be set to one for
the purpose of obtaining a program-check indication.Input/Output Operations 21 t
The channel command word (CCW) specifies the
command to be executed and, for commands initiat
ing
associated with the operation and the action to be
taken whenever transfer to or from the area is com
pleted. The CCWs can be located anywhere in main
storage, and more than one can be associated with a
START
The first CCW is fetched during the execution of
ST ART
executed as START
RELEASE is executed independently of the device,
the first CCW is fetched subsequent to the execution
of START
CCW in the sequence is obtained when the opera
tion has progressed to the point where the additional
CCW is needed. Fetching of the CCWs by the chan
nel does not affect the contents of the location in
main storage.
The CCW has the following format:
Command
Code
o 8
48
31
Count
The fields in the CCW are allocated for the follow
ing purposes:
be performed.
63
Data Address: Bits 8-31 specify the location of an
eight-bit byte in absolute main storage. It is the first
location referred to in the area designated by the
CCW.
Chain-Data (CD) Flag: Bit 32, when one, specifies
chaining of data. It causes the storage area designat
ed by the next CCW to be used with the current
operation.
Chain-Command (CC) Flag: Bit 33, when one, and
when the CD flag is zero, specifies chaining of com
mands. It causes the operation specified by the com
mand code in the next CCW to be initiated on nor
mal completion of the current operation.
Suppress-Length-Indication (SLI) Flag: Bit 34 con
trols whether an incorrect-length condition is to be
indicated to the program. When this bit is one and
the CD flag is zero, the incorrect-length indication is
suppressed. When both the CC and SLI flags are
one, command chaining takes place regardless of the
presence of an incorrect-length condition.
Skip (SKIP) Flag: Bit 35, when one, specifies sup
pression of transfer of information to storage during
a read, read backward, or sense operation.
Program-Controlled-Interruption (PCI) Flag: Bit
36, when one, causes the channel to generate an
interruption condition when the CCW takes control
of the channel. When bit 36 is zero, normal opera
tion takes place.
Indirect Data
one, specifies indirect data addressing. (The flag is
valid in both BC and EC modes.)
Count: Bits 48-63 specify the number of eight-bit
byte locations in the storage area designated by the
CCW.
Bit positions 38-39 of every CCW other than one
specifying transfer in channel must contain zeros.
Additionally, if indirect addressing is specified, bits
boundary, and bits
rect data address list must be zeros. (See "Channel
Indirect Data Addressing.")
check condition is generated. When the first CCW
designated by the CAW does not contain the re
quired zeros, the
the status portion of the CSW with the program
check indication is stored during execution of
ST ART
condition during data chaining causes the
to be signaled to conclude the operation. When the
absence of these zeros is detected during command
chaining or subsequent to the execution of START
initiated, and an interruption condition is generated.
The contents of bit positions
are ignored.
Programming Note
Bit positions 38-39 of the CCW, which presently
must contain zeros, may in the future be assigned for
the control of new functions. It is therefore recom
mended that these bit positions not be set to one for
the purpose of obtaining a program-check indication.