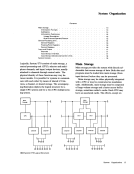
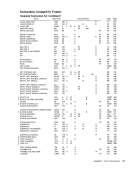
Channel Data Check
Channel data check indicates that a machine error
has been detected in the information transferred to
or from main storage during anI/O operation, or
that a parity error has been detected on the data on
bus-in during an input operation. This information
includes the data read or written, as well as the in
formation transferred as data during a sense or con
trol operation. The error may have been detected
anywhere inboard of theI/O interface: in the chan
nel, in main storage, or on the path between the two.
Channel data check may be indicated for data with
an invalid checking block code (CBC) in main stor
age when that data is referred to by the channel but
does not participate in the operation.
Whenever a parity error onI/O input data is indi
cated by means of channel data check, the channel
forces correct parity on all data received over theI/O interface, and all data placed in main storage
has valid CBC. When, on an input operation, the
channel attempts to store less than a complete
checking block, and invalid CBC is detected on the
checking block in storage, the contents of the loca
tion remain unchanged, with invalid CBC.On an
output operation, whenever a channel data check is
indicated, all bytes that came from a checking block
with invalid CBC have been transmitted on the in
terface with parity errors.
A condition indicated as channel data check caus
es command chaining to be suppressed, but does not
affect the execution of the current operation. Data
transfer proceeds to normal completion, if possible,
and anI/O interruption condition is generated when
the device presents channel end. A logout may be
performed, depending on the channel. Accordingly,
the detection of the error may affect the state of the
channel and the device.
Channel Control Check
Channel control check is caused by any machine
malfunctioning affecting channel controls. The con
dition includes invalid CBC on CCW and data ad
dresses and invalid CBC on the contents of the
CCW. The condition also includes those channel
detected errors associated with data transfer that are
not indicated as channel data check, as well as thoseI/O interface errors detected by the channel that are
not indicated as interface control check. Conditions
responsible for channel control check may cause the
contents of the CSW to to invalid and conflicting.
The CSW as generated by the channel has valid
CBC.
Detection of the channel-control-check condition
causes the current operation, if any, to be immedi
ately concluded.
In some situations, the channel-control-check
condition may be reported as an external-damage or
system-damage machine-check condition. Channel
control check is set whenever CSW bit S, logout
pending, is set.
Interface Control Check
Interface control check indicates that an invalidsig nal has occurred on the I/O interface. The condi
tion is detected by the channel and ususally indicates
malfunctioning of anI/O device. It can be due to
the following reasons:
1. The address or status byte received from a de
vice has invalid parity.
2. A device responded with an address other than
the address specified by the channel during
initiation of an operation.
3. During command chaining the device appeared
not operational.
4. A signal from a device occurred at an invalid
time or had invalid duration.
S. A device signaledI/O error alert by raising the
disconnect-in-line on theI/O interface.
Detection of the interface control check condition
causes the current operation, if any, to be immedi
ately concluded.
Chaining Check
Chaining check is caused by channel overrun during
data chaining on input operations. The condition
occurs when theI/O data rate is too high for the
particular resolution of data addresses. Chaining
check cannot occur on output operations.
Detection of the chaining-check condition causes
theI/O device to be signaled to conclude the opera
tion. It causes command chaining to be suppressed.
Contents of Channel Status Word
The contents of the CSW depend on the condition
causing the storing of the CSW and on the program
ming method by which the information is obtained.
The status portion always identifies the condition
that caused storing of the CSW. The protection key,
command address, and count fields may contain
information pertaining to the last operation or may
be set to zero, or the original contents of these fields
at location 64 may be left unchanged.
Information Provided by Channel Status Word
Conditions associated with the execution or conclud
ing of an operation at the subchannel cause the
whole CSW to be replaced. Such a CSW can be
stored only by anI/O interruption or by TEST I/O Input/Output Operations 235
Channel data check indicates that a machine error
has been detected in the information transferred to
or from main storage during an
that a parity error has been detected on the data on
bus-in during an input operation. This information
includes the data read or written, as well as the in
formation transferred as data during a sense or con
trol operation. The error may have been detected
anywhere inboard of the
nel, in main storage, or on the path between the two.
Channel data check may be indicated for data with
an invalid checking block code (CBC) in main stor
age when that data is referred to by the channel but
does not participate in the operation.
Whenever a parity error on
cated by means of channel data check, the channel
forces correct parity on all data received over the
has valid CBC. When, on an input operation, the
channel attempts to store less than a complete
checking block, and invalid CBC is detected on the
checking block in storage, the contents of the loca
tion remain unchanged, with invalid CBC.
output operation, whenever a channel data check is
indicated, all bytes that came from a checking block
with invalid CBC have been transmitted on the in
terface with parity errors.
A condition indicated as channel data check caus
es command chaining to be suppressed, but does not
affect the execution of the current operation. Data
transfer proceeds to normal completion, if possible,
and an
the device presents channel end. A logout may be
performed, depending on the channel. Accordingly,
the detection of the error may affect the state of the
channel and the device.
Channel Control Check
Channel control check is caused by any machine
malfunctioning affecting channel controls. The con
dition includes invalid CBC on CCW and data ad
dresses and invalid CBC on the contents of the
CCW. The condition also includes those channel
detected errors associated with data transfer that are
not indicated as channel data check, as well as those
not indicated as interface control check. Conditions
responsible for channel control check may cause the
contents of the CSW to to invalid and conflicting.
The CSW as generated by the channel has valid
CBC.
Detection of the channel-control-check condition
causes the current operation, if any, to be immedi
ately concluded.
In some situations, the channel-control-check
condition may be reported as an external-damage or
system-damage machine-check condition. Channel
control check is set whenever CSW bit S, logout
pending, is set.
Interface Control Check
Interface control check indicates that an invalid
tion is detected by the channel and ususally indicates
malfunctioning of an
the following reasons:
1. The address or status byte received from a de
vice has invalid parity.
2. A device responded with an address other than
the address specified by the channel during
initiation of an operation.
3. During command chaining the device appeared
not operational.
4. A signal from a device occurred at an invalid
time or had invalid duration.
S. A device signaled
disconnect-in-line on the
Detection of the interface control check condition
causes the current operation, if any, to be immedi
ately concluded.
Chaining Check
Chaining check is caused by channel overrun during
data chaining on input operations. The condition
occurs when the
particular resolution of data addresses. Chaining
check cannot occur on output operations.
Detection of the chaining-check condition causes
the
tion. It causes command chaining to be suppressed.
Contents of Channel Status Word
The contents of the CSW depend on the condition
causing the storing of the CSW and on the program
ming method by which the information is obtained.
The status portion always identifies the condition
that caused storing of the CSW. The protection key,
command address, and count fields may contain
information pertaining to the last operation or may
be set to zero, or the original contents of these fields
at location 64 may be left unchanged.
Information Provided by Channel Status Word
Conditions associated with the execution or conclud
ing of an operation at the subchannel cause the
whole CSW to be replaced. Such a CSW can be
stored only by an