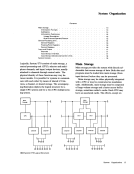
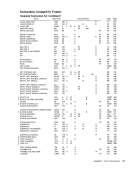
Condition Channel control check
Status stored by STARTI/O or START I/O FAST RELEASE
Status stored by HALTI/O or HALT DEVICE Invalid CCW address specified in transfer in channel (TIC) Invalid CCW address in TIC Invalid CCW address generated Invalid command code Invalid count Invalid data address I nval id CCW format Invalid sequence - 2 TICs Protection check
Chaining check
Termination under countcontrol Termination by I/O device
Termination by HALTI/O Termination by CLEAR I/O .,
Suppression of command chaining due to unit check or unit
exception with device end orcontrol unit end
Termination on command chaining by busy, unit check, or
unit exception
Deferred condition code 1 for STARTI/O FAST RELEASE PCI flag in CCW I nterface control check Channel end after HALT I/O on selector channel Channel end after CLEAR I/O Control unit end
Device end
Attention
Busy
Status modifier
Contents of the CSW Command Address Field
concluded, the difference between the original count
in the CCW and the residual count in theCSW is
equal to the number of bytes transferred to main
storage; on an output operation, the difference is
equal to the number of bytes transferred to theI/O device.
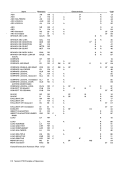
The following table lists the contents of the count
field for all conditions that can cause theCSW to be
stored. The conditions are listed in the order of pri
ority; that is, if two conditions ate indicated or oc
cur, theCSW appears as for the condition higher on
the list.
Status
The status bits identify the conditions that have been
detected during theI/O operation, that have caused
a command to be rejected, or that have been gener
ated by external events.
When the channel detects several error condi
tions, all conditions may be indicated or only one
Contents ofField Unpredictable
Unchanged
Unchanged
Address ofTIC + 8
Address ofTIC + 8
Firstinvalid CCW address + 8
Address ofinvalid CCW + 8
Address ofinvalid CCW + 8
Address ofinvalid CCW + 8
Address ofinvalid CCW + 8
Address of secondTIC + 8
Address of protectedCOW + 8
Address oflast-used CCW + last-used CCW + 8
Address oflast-used CCW + 8
Address oflast-used CCW + 8
Address oflast-used CCW + 8
Address oflast CCW used in the completed operation + 8
Address of CCW specifying the new operation + 8
Address of CCW specifying the new operation + 8
Address oflast-used CCW + 8
UnpredictableZero Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero Zero may appear in the CSW, depending on the condition
and model. Conditions associated with equipment
malfunctioning have precedence, and whenever mal
functioning causes an operation to be terminated,
channel control check, interface control check, or
channel data check is indicated, depending on the
condition. When an operation is concluded by pro
gram check, protection check, or chaining check, the
channel identifies the condition responsible for the
concluding and mayor may not indicate incorrect
length. When a data error has been detected and the
operation is concluded prematurely because of a
program check, protection check, or chaining check,
both data check and the programming error are
identified.
If the CCW fetched on command chaining con
tains thePCI flag but a programming error in the
contents of the CCW precludes the initiation of the
operation, whether thePCI bit appears in the CSW associated with the interruption condition is unpre
dictable. Similarly, if a programming error in the
Input/Output Operations 237
Status stored by START
Status stored by HALT
Chaining check
Termination under count
Termination by HALT
Suppression of command chaining due to unit check or unit
exception with device end or
Termination on command chaining by busy, unit check, or
unit exception
Deferred condition code 1 for START
Device end
Attention
Busy
Status modifier
Contents of the CSW Command Address Field
concluded, the difference between the original count
in the CCW and the residual count in the
equal to the number of bytes transferred to main
storage; on an output operation, the difference is
equal to the number of bytes transferred to the
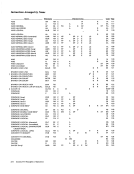
The following table lists the contents of the count
field for all conditions that can cause the
stored. The conditions are listed in the order of pri
ority; that is, if two conditions ate indicated or oc
cur, the
the list.
Status
The status bits identify the conditions that have been
detected during the
a command to be rejected, or that have been gener
ated by external events.
When the channel detects several error condi
tions, all conditions may be indicated or only one
Contents of
Unchanged
Unchanged
Address of
Address of
First
Address of
Address of
Address of
Address of
Address of second
Address of protected
Address of
Address of
Address of
Address of
Address of
Address of CCW specifying the new operation + 8
Address of CCW specifying the new operation + 8
Address of
Unpredictable
and model. Conditions associated with equipment
malfunctioning have precedence, and whenever mal
functioning causes an operation to be terminated,
channel control check, interface control check, or
channel data check is indicated, depending on the
condition. When an operation is concluded by pro
gram check, protection check, or chaining check, the
channel identifies the condition responsible for the
concluding and mayor may not indicate incorrect
length. When a data error has been detected and the
operation is concluded prematurely because of a
program check, protection check, or chaining check,
both data check and the programming error are
identified.
If the CCW fetched on command chaining con
tains the
contents of the CCW precludes the initiation of the
operation, whether the
dictable. Similarly, if a programming error in the
Input/Output Operations 237