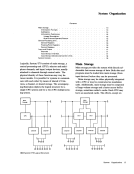
and stopped states. The key is not effective when the CPU is in the check-stop state.
Start Key
Activating the start key causes theCPU to enter the
operating state.See "Stopped and Operating States" in the chapter "System Control." The key is effec
tive only when theCPU is in the stopped state, and
the effect is unpredictable when the stopped state
has been entered by reset.
Stop Key
Activating the stop key causes theCPU to perform
the stop function.See "Stopped and Operating States" in the chapter "System ControL" The stop key is effective only while the CPU is in
the operating state.
Operation Note
Activating the stop key has no effect when a contin
uousstring of interruptions occurs, when the prefix
register contains an invalid address, or when theCPU is unable to complete an instruction because of
a machine malfunction.
Store-Status Key
Activating the store-status key initiates the store
status function. Although the store-status function is
performed compatibly on all models, the initiation of
the function differs among models.Some models
initiate the function by the use of a special keyboard
mnemonic and some by the use of a pushbutton,
while others may provide a CRT -menu selection.See "Store Status" in the chapter "System Con trol" for a description of the function.
The manual control for performing store status is
effective only when theCPU is in the stopped state.
Operation Note
The store-status function would ordinarily be used in
conjunction with a standalone,dump program for the
analysis of program malfunctions. For such an oper
ation, the following sequence would be called for:• Activating of the system-reset key. • Initiation of the store-status function. • Normal IPL of a standalone dump program.
System Indicator
The system indicator is on when theCPU cluster
meter or customer-engineer meter is running.
System-Reset Key
Activating the system-reset key causes a reset func
tion to be performed. Whether the enable-system
clear key is activated at the same time determines
the type of reset and the resultant effect on the sys
tem. In a multiprocessing system, the effect of the
key is propagated to allCPUs configured, for reset
purposes, to thisCPU. See the detailed discussion
under"Resets" in the chapter "System Control." Activating the system-reset key may change the
configuration, including the connection with chan
nels, storage units, and otherCPUs. The key is effective while power is on the system.
Test Indicator
The test indicator is on when a manual control is not
in its normal position or when a maintenance func
tion is being performed for theCPU, channels, or
storage.
The test indicator is on whenever a control on the
system control panel or on any separate maintenance
panel for theCPU, storage, or channels is in an ab
normal position that can affect the normal operation
of a program.
The test indicator may be on when one or more
diagnostic functions under control ofDIAGNOSE are activated or when certain abnormal circuit
breaker or thermal conditions occur.
The test indicator does not reflect the state of
marginal voltage controls.
Thermal/CB Power-Check Indicator
The thermal! CB power-check indicator, which is
one or more red lights, goes on when a thermal con
dition, a circuit-breaker-trip condition, or both con
ditions are detected in theCPU complex. This indi
cator is turned off from the customer-engineer
power-control panel.TOD Clock Key
The TaD (time-of-day) clock key provides an inter
lock in the execution of the instructionSET CLOCK for the purpose of guarding against an unauthorized
or inadvertent change to the time-of-day clock val
ue.
When the TaD clock key is not activated, that is,
is in the position labeled"secure," the value of the
TaD clock is protected against alteration by the
program, and the execution of SETCLOCK does
not change the value of the clock.
When the TaD clock key is activated, that is, is in
the position labeled"enable set," alteration of the
clock value by means of SETCLOCK is permitted.
System Console 247
Start Key
Activating the start key causes the
operating state.
tive only when the
the effect is unpredictable when the stopped state
has been entered by reset.
Stop Key
Activating the stop key causes the
the stop function.
the operating state.
Operation Note
Activating the stop key has no effect when a contin
uous
register contains an invalid address, or when the
a machine malfunction.
Store-Status Key
Activating the store-status key initiates the store
status function. Although the store-status function is
performed compatibly on all models, the initiation of
the function differs among models.
initiate the function by the use of a special keyboard
mnemonic and some by the use of a pushbutton,
while others may provide a CRT -menu selection.
The manual control for performing store status is
effective only when the
Operation Note
The store-status function would ordinarily be used in
conjunction with a standalone
analysis of program malfunctions. For such an oper
ation, the following sequence would be called for:
System Indicator
The system indicator is on when the
meter or customer-engineer meter is running.
System-Reset Key
Activating the system-reset key causes a reset func
tion to be performed. Whether the enable-system
clear key is activated at the same time determines
the type of reset and the resultant effect on the sys
tem. In a multiprocessing system, the effect of the
key is propagated to all
purposes, to this
under
configuration, including the connection with chan
nels, storage units, and other
Test Indicator
The test indicator is on when a manual control is not
in its normal position or when a maintenance func
tion is being performed for the
storage.
The test indicator is on whenever a control on the
system control panel or on any separate maintenance
panel for the
normal position that can affect the normal operation
of a program.
The test indicator may be on when one or more
diagnostic functions under control of
breaker or thermal conditions occur.
The test indicator does not reflect the state of
marginal voltage controls.
Thermal/CB Power-Check Indicator
The thermal! CB power-check indicator, which is
one or more red lights, goes on when a thermal con
dition, a circuit-breaker-trip condition, or both con
ditions are detected in the
cator is turned off from the customer-engineer
power-control panel.
The TaD (time-of-day) clock key provides an inter
lock in the execution of the instruction
or inadvertent change to the time-of-day clock val
ue.
When the TaD clock key is not activated, that is,
is in the position labeled
TaD clock is protected against alteration by the
program, and the execution of SET
not change the value of the clock.
When the TaD clock key is activated, that is, is in
the position labeled
clock value by means of SET
System Console 247