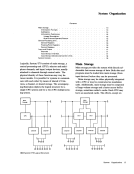
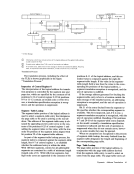
Where more than one page-reference is given, major references
appear first.
absolute address 95, 14
absolute main storage 92
access control bits (in key in storage) 38
access exception80 handling of (table) 81
priority of 83
recognition of80 recognition of (table) 83
access to main storage, right of 38
accesses (references), sequence of main storage 23
active, state of address translation table entry 65
adapter, channel-to-channel 186
ADD (A, AR) instruction 117
ADD DECIMAL(AP) instruction 149
example305 ADD HALFWORD (AH) instruction 117
example 291
ADDLOGICAL (AL, ALR) instruction 120 ADD NORMALIZED (ADR, AD, AER, AE) instruction 160 example 309 ADD NORMALIZED (AXR) instruction 160 ADD UNNORMALIZED (AWR, AW, AUR, AU) instruction 162
example309 address
absolute 95, 14
base 21
branch 22
channel/device 192
failing-storage (see failing-storage address)
invalid 77
logical 14,58
of channel command word, inCSW 229
-real 95, 14, 57
translation (see dynamic address translation)
virtual 57
address arithmetic (generation) 21
address-compare controls 244
address generation 21
address identification,CPU 101 addresses
handling of 63
translated (see dynamic address translation)
types of 62
addressing
capability 14
information in a register20 limitations of 14
main storage 14
wraparound 14
addressing exception 76,15
during address translation 61,62,81
summary table 77
. addressing,I/O channel 191
device 191
nonexistent or protected areas 213
PageofGA22-7000-4 Revised September 1, 1975
By TNL: GN22-0498
alert condition (machine-check interruption) 175
degradation 179
warning 179
alteration mask for program-event recording40 alteration of an instruction by EXECUTE 129
AND (NR, N, NI, NC) instruction120 example 292 Index arithmetic (see decimal instructions; floating-point-instructions;
general instructions)
assembly language, symbolic operand designations forSystem/370 (see individual instruction descriptions)
assigned main storage locations90 absolute 91
real90 asynchronous fixed logout (see machine-check fixed logout)
asynchronous fixed logout control bit (in control register 14) 182
asynchronous machine-check logout (see machine-check extended
logout and machine-check fixed logout)
asynchronous MCEL control bit (in controlregister 14) 182
attached, state of address translation table entry 65
attachment ofI/O devices 186
attention(I/O unit status condition) 229,239
availability, System/370 facilities for achieving 11
available(I/O system state) 193
B field of an instruction20,21 backed-up bit (machine-check interruption code) 179
base address (in operand designation) 21
basic-control mode 31PSW format 33
(see also extended-control mode)
BC mode (see basic-control mode)
binary notation, excess-64 159
bit, check 14
bits ina byte 14
block-concurrent references to storage 27
block of data,I/O definition 210 self-describing 214
block-multiplexer channel 188
block-multiplexing-control bit 189
block-multiplexing mode bit (in control register0) 189
blocking of data(I/O operations) 210 boundaries in main storage, integral 15
branch address 22
BRANCH AND LINK (BAL, BALR) instruction 121
example 292
BRANCHON CONDITION (BC, BCR) instruction 121
example 292
BRANCHON COUNT (BCT, BCTR) instruction 122
example 293
BRANCHON INDEX HIGH (BXH) instruction 122
example 293
BRANCHON INDEX LOW OR EQUAL (BXLE) instruction 123
example 293
branch, successful (program event) 42
branching, general description of 22
burst mode 187
bus out check (sense data)220 Index 315
appear first.
absolute address 95, 14
absolute main storage 92
access control bits (in key in storage) 38
access exception
priority of 83
recognition of
access to main storage, right of 38
accesses (references), sequence of main storage 23
active, state of address translation table entry 65
adapter, channel-to-channel 186
ADD (A, AR) instruction 117
ADD DECIMAL
example
example 291
ADD
example
absolute 95, 14
base 21
branch 22
channel/device 192
failing-storage (see failing-storage address)
invalid 77
logical 14,58
of channel command word, in
-real 95, 14, 57
translation (see dynamic address translation)
virtual 57
address arithmetic (generation) 21
address-compare controls 244
address generation 21
address identification,
handling of 63
translated (see dynamic address translation)
types of 62
addressing
capability 14
information in a register
main storage 14
wraparound 14
addressing exception 76,15
during address translation 61,62,81
summary table 77
. addressing,
device 191
nonexistent or protected areas 213
Page
By TNL: GN22-0498
alert condition (machine-check interruption) 175
degradation 179
warning 179
alteration mask for program-event recording
AND (NR, N, NI, NC) instruction
general instructions)
assembly language, symbolic operand designations for
assigned main storage locations
real
asynchronous fixed logout control bit (in control register 14) 182
asynchronous machine-check logout (see machine-check extended
logout and machine-check fixed logout)
asynchronous MCEL control bit (in controlregister 14) 182
attached, state of address translation table entry 65
attachment of
attention
availability, System/
available
B field of an instruction
base address (in operand designation) 21
basic-control mode 31
(see also extended-control mode)
BC mode (see basic-control mode)
binary notation, excess-64 159
bit, check 14
bits in
block-concurrent references to storage 27
block of data,
block-multiplexer channel 188
block-multiplexing-control bit 189
block-multiplexing mode bit (in control register
blocking of data
branch address 22
BRANCH AND LINK (BAL, BALR) instruction 121
example 292
BRANCH
example 292
BRANCH
example 293
BRANCH
example 293
BRANCH
example 293
branch, successful (program event) 42
branching, general description of 22
burst mode 187
bus out check (sense data)