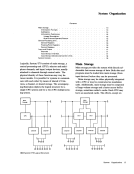
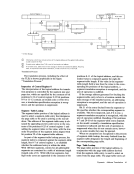
CPU. The assignment and definition of order codes
appears in the chapter"Multiprocessing." The 16-bit binary number contained in bit posi
tions 16-31 of the general register designated by the
R3 field forms the processor address. The high-order
16 bits of the register are ignored.
A serialization function is performed.CPU oper
ation is delayed until all previous accesses by thisCPU to main storage have been completed, as ob
served by channels and other CPUs, and then the
signaling occurs. No subsequent instructions or their
operands are accessed by thisCPU until the execu
tion of the instruction is completed.
When the order code is accepted and no nonzero
status is returned, condition code0 is set. When
status information is generated by thisCPU or re
turned by the addressed CPU, the status is placed in
the general register designated by the Rl field, and
condition code 1 is set.
When the access path to the addressedCPU is
busy or the addressedCPU is operational and in a
state where it cannot respond to the order code,
condition code 2 is set.
When the addressedCPU is not operational (that
is, it is not provided, or it is not configured to this
CPU, or it is in certain customer-engineer test modes,
or its power is off), condition code 3 is set.
A more detailed discussion of the condition-code
settings for SIGNALPROCESSOR is contained in
the chapter"Multiprocessing." Resulting Condition Code:
oOrder code accepted
1 Status stored
2 Busy
3 Not operationalProgram Exceptions:
Operation (if the multiprocessing feature is not
installed)
Privileged operation
Programming Notes
The execution time on the issuingCPU for SIG NAL PROCESSOR may vary depending on the
model, the order code, and the state of the addressed
CPU. In some cases, the execution time may be sev
eral seconds.
To ensure that presently written programs will be
executed properly when new facilities using addi
tional bits are installed, only zeros should appear in
the unused bit positions of the second-operand ad
dress and in bit positions0-15 of the register desig-
nated by the R3 field.Store Clock Comparator 8207 o 16 20 31
The current value of the clock comparator is stored
at the doubleword designated by the second-operand
address.
Zeros are provided for the rightmost bit positions
that are not used for comparison with the time-of
day clock.
The operand must be designated on a doubleword
boundary; otherwise, a specification exception is
recognized, and the operation is suppressed. The
operation is suppressed on protection and addressing
exceptions.
Condition Code: The code remains unchanged.Program Exceptions:
Operation (if the clock comparator is not in-
stalled)
Privileged operation
Access (store, operand 2)
SpecificationStore Control
STCTL Rl,R3,D2(B2)I B6
o 8 12 16[RS] 20 31
The set of control registers starting with the control
register designated by the Rl field and ending with
the control register designated by the R3 field is
stored at the locations designated by the second
operand address.
The storage area where the contents of the con
trol registers are placed starts at the location desig
nated by the second-operand address and continues
through as many storage words as the number of
control registers specified. The contents of the con
trol registers are stored in ascending order of their
addresses, starting with the control register designat
ed by the Rl field and continuing up to and includ
ing the control register designated by the R3 field,
with control register0 following control register 15.
The contents of the control registers remain un
changed.
System-Control Instructions 111
appears in the chapter
tions 16-31 of the general register designated by the
R3 field forms the processor address. The high-order
16 bits of the register are ignored.
A serialization function is performed.
ation is delayed until all previous accesses by this
served by channels and other CPUs, and then the
signaling occurs. No subsequent instructions or their
operands are accessed by this
tion of the instruction is completed.
When the order code is accepted and no nonzero
status is returned, condition code
status information is generated by this
turned by the addressed CPU, the status is placed in
the general register designated by the Rl field, and
condition code 1 is set.
When the access path to the addressed
busy or the addressed
state where it cannot respond to the order code,
condition code 2 is set.
When the addressed
is, it is not provided, or it is not configured to this
CPU, or it is in certain customer-engineer test modes,
or its power is off), condition code 3 is set.
A more detailed discussion of the condition-code
settings for SIGNAL
the chapter
o
1 Status stored
2 Busy
3 Not operational
Operation (if the multiprocessing feature is not
installed)
Privileged operation
Programming Notes
The execution time on the issuing
model, the order code, and the state of the addressed
CPU. In some cases, the execution time may be sev
eral seconds.
To ensure that presently written programs will be
executed properly when new facilities using addi
tional bits are installed, only zeros should appear in
the unused bit positions of the second-operand ad
dress and in bit positions
nated by the R3 field.
The current value of the clock comparator is stored
at the doubleword designated by the second-operand
address.
Zeros are provided for the rightmost bit positions
that are not used for comparison with the time-of
day clock.
The operand must be designated on a doubleword
boundary; otherwise, a specification exception is
recognized, and the operation is suppressed. The
operation is suppressed on protection and addressing
exceptions.
Condition Code: The code remains unchanged.
Operation (if the clock comparator is not in-
stalled)
Privileged operation
Access (store, operand 2)
Specification
STCTL Rl,R3,D2(B2)
o 8 12 16
The set of control registers starting with the control
register designated by the Rl field and ending with
the control register designated by the R3 field is
stored at the locations designated by the second
operand address.
The storage area where the contents of the con
trol registers are placed starts at the location desig
nated by the second-operand address and continues
through as many storage words as the number of
control registers specified. The contents of the con
trol registers are stored in ascending order of their
addresses, starting with the control register designat
ed by the Rl field and continuing up to and includ
ing the control register designated by the R3 field,
with control register
The contents of the control registers remain un
changed.
System-Control Instructions 111