Channel Model Number
o 4
MaximumIOEL Length
31
Bits0-3 specify the channel type. When a channel
can operate as more than one type, the code stored
identifies the channel type at the time the instruction
is executed. The following codes are assigned:0000 Selector 0001 Byte multiplexer 0010 Block multiplexer
Bits 4-15 identify the channel model. When the
channel model is implied by the channel type and theCPU model, zeros are stored in the field.
Bits 16-31 contain the length in bytes of the long
estI/O extended logout that can be stored by the
channel during anI/O interruption. If the channel
never stores logout information using the10EL pointer, then this field is set to zero.
When the channel detects an equipment malfunc
tion during the execution ofSTORE CHANNEL
ID, the channel causes the status portion, bits 32-47,
of the CSW to be replaced by a new set of status
bits. With the exception of the channel control check
bit (bit 45), which is stored as a one, all bits in the
status field are stored as zeros. The contents of the
other fields of theCSW are not changed.
WhenSTORE CHANNEL ID cannot be execut
ed because of a pending logout condition which af
fects the operational capability of the channel, a fullCSW is stored. The fields in the CSW are all set to
zero, with the exception of the logout-pending bit
and the channel control check bit, which are set to
ones. No channel logout is associated with this sta
tus.
Program Exceptions:
Privileged operation
Resulting Condition Code:
o Channel ID correctly stored
1CSW stored
2 Channel activity prohibited storing ID
3 Not operational
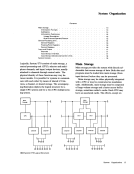
The condition code set bySTORE CHANNEL
ID for all possible states of theI/O system is shown
graphically as follows.See "States of the
Input/Output System" for a detailed definition of
the A, I, W, and N states.
A W N
Channel
o $ $ 3
AAvailable I Interruption pending
W Working
N
Not operational
$ When the channel is unable to store the channel10 because
of its working state or because it contains a pendinginter ruption condition, a condition code 2 is set. If the working
or interruption pending state does not preclude the storing
of the channelID, a condition code 0 is set.
Condition Codes Set by STORE CHANNEL ID
Test Channel
TCH[S] 9FOO o 16 20 31
The condition code in thePSW is set to indicate the
state of the addressed channel. The state of the
channel is not affected, and no action is caused. Bits
8-15 of the instruction are ignored.
The instruction TEST CHANNEL is executed
only when theCPU is in the supervisor state.
Bits 16-23 of the second-operand address identify
the channel to which the instruction applies. Bit posi
tions 24-31 of the address are ignored.
The instruction TEST CHANNEL inspects only
the state of the addressed channel. It tests whether
the channel is operating in the burst mode, is aware
of any outstanding interruption conditions from its
devices, or is not operational. When the channel is
operating in the burst mode and contains a pending
interruption condition, the condition code is set as
for operation in the burst mode. When none of these
conditions exist, the available state is indicated. No
device is selected and, on the multiplexer channel,
the sub channels are not interrogated.
Program Exceptions:
Privileged operation
Resulting Condition Code:
o Channel available
1 Interruption or logout condition pending in
channel
2 Channel operating in burst mode
3 Channel not operational
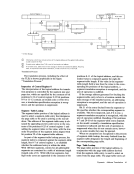
The condition code set by TEST CHANNEL for
all possible states of the addressed channel is shown
Input/Output Operations207
o 4
Maximum
31
Bits
can operate as more than one type, the code stored
identifies the channel type at the time the instruction
is executed. The following codes are assigned:
Bits 4-15 identify the channel model. When the
channel model is implied by the channel type and the
Bits 16-31 contain the length in bytes of the long
est
channel during an
never stores logout information using the
When the channel detects an equipment malfunc
tion during the execution of
ID, the channel causes the status portion, bits 32-47,
of the CSW to be replaced by a new set of status
bits. With the exception of the channel control check
bit (bit 45), which is stored as a one, all bits in the
status field are stored as zeros. The contents of the
other fields of the
When
ed because of a pending logout condition which af
fects the operational capability of the channel, a full
zero, with the exception of the logout-pending bit
and the channel control check bit, which are set to
ones. No channel logout is associated with this sta
tus.
Program Exceptions:
Privileged operation
Resulting Condition Code:
o Channel ID correctly stored
1
2 Channel activity prohibited storing ID
3 Not operational
The condition code set by
ID for all possible states of the
graphically as follows.
Input/
the A, I, W, and N states.
A W N
Channel
o $ $ 3
A
W Working
N
Not operational
$ When the channel is unable to store the channel
of its working state or because it contains a pending
or interruption pending state does not preclude the storing
of the channel
Condition Codes Set by STORE CHANNEL ID
Test Channel
TCH
The condition code in the
state of the addressed channel. The state of the
channel is not affected, and no action is caused. Bits
8-15 of the instruction are ignored.
The instruction TEST CHANNEL is executed
only when the
Bits 16-23 of the second-operand address identify
the channel to which the instruction applies. Bit posi
tions 24-31 of the address are ignored.
The instruction TEST CHANNEL inspects only
the state of the addressed channel. It tests whether
the channel is operating in the burst mode, is aware
of any outstanding interruption conditions from its
devices, or is not operational. When the channel is
operating in the burst mode and contains a pending
interruption condition, the condition code is set as
for operation in the burst mode. When none of these
conditions exist, the available state is indicated. No
device is selected and, on the multiplexer channel,
the sub channels are not interrogated.
Program Exceptions:
Privileged operation
Resulting Condition Code:
o Channel available
1 Interruption or logout condition pending in
channel
2 Channel operating in burst mode
3 Channel not operational
The condition code set by TEST CHANNEL for
all possible states of the addressed channel is shown
Input/Output Operations