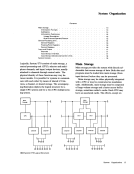
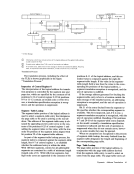
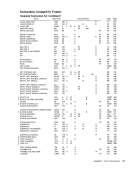
Word
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
2
8
9
9
9
9
9
10
11
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
15
Bits0 2
8-9
10
11-12
16
17
18
19
20
21
24
25
26
0-7
8-25
0-31
16-310 2
3
16-31
8-31
8-310 2
4
5
6
7
8
9
8-28
Explanation:
Name of field
Block-Multiplexing ControlSSM-Suppression Control TOD Clock Sync Control
Page-Size Control
Unassigned, must be zeroSegment-Size Control
Malfunction-Alert Mask
Emergency-Signal Mask1 "',' , External-Call Mask ..
Clock-Comparator Mask
CPU-Timer MaskInterval-Timer Mask
Interrupt-Key Mask
External-Signal MaskSe£ment-Table Length Segment"Table Address
Channel Masks
Monitor Masks
Successful-Branching Event Mask
Instruction-fetching-Event Mask
Storage-Alteration-Event Mask
GR-Alteration-Event Mask
PER 1 General Register Masks
PER Starting Address
PER Ending Address
Check-Stop Control
Synchronous-MCE L
2
Control
I/O-Extended-Logout Control
Recovery-Report Mask
Degradation-Report Mask
External-Damage-Report Mask
Warning Mask
Asynchronous-MCEL Control
Asynchronous-Fixed-Log Control
MCEL Address
The fields not listed are unassigned.
Associated With
Block-MultiplexingSSM Suppression
Multiprocessing
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing
Clock Comparator
CPU Timer
Interval Timer
Interrupt Key
ExternalSignal Dynamic Addr. Translation
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Channels
Monitoring
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check HandlingI/O Extended Logout
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Except for bit 10 of control register 0, the initial value of unassigned register positions is unpredictable.
1 PER means program-event recording.
2 MCEL means machine-check extended logout.
3 Bit 22 is set to one, with all other bits set to zero, thus yielding a decimal byte address of 512.
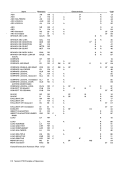
Assignment of Control Registel' FieldsInitial Value
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
1
o
o
o
o
o
o
512
3
System Control 37
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
2
8
9
9
9
9
9
10
11
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
15
Bits
8-9
10
11-12
16
17
18
19
20
21
24
25
26
0-7
8-25
0-31
16-31
3
16-31
8-31
8-31
4
5
6
7
8
9
8-28
Explanation:
Name of field
Block-Multiplexing Control
Page-Size Control
Unassigned, must be zero
Malfunction-Alert Mask
Emergency-Signal Mask
Clock-Comparator Mask
CPU-Timer Mask
Interrupt-Key Mask
External-Signal Mask
Channel Masks
Monitor Masks
Successful-Branching Event Mask
Instruction-fetching-Event Mask
Storage-Alteration-Event Mask
GR-Alteration-Event Mask
PER 1 General Register Masks
PER Starting Address
PER Ending Address
Check-Stop Control
Synchronous-MCE L
2
Control
I/O-Extended-Logout Control
Recovery-Report Mask
Degradation-Report Mask
External-Damage-Report Mask
Warning Mask
Asynchronous-MCEL Control
Asynchronous-Fixed-Log Control
MCEL Address
The fields not listed are unassigned.
Associated With
Block-Multiplexing
Multiprocessing
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing
Clock Comparator
CPU Timer
Interval Timer
Interrupt Key
External
Dynamic Addr. Translation
Channels
Monitoring
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Program-Event Recording
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Machine-Check Handling
Except for bit 10 of control register 0, the initial value of unassigned register positions is unpredictable.
1 PER means program-event recording.
2 MCEL means machine-check extended logout.
3 Bit 22 is set to one, with all other bits set to zero, thus yielding a decimal byte address of 512.
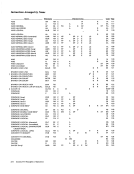
Assignment of Control Registel' Fields
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
1
o
o
o
o
o
o
512
3
System Control 37