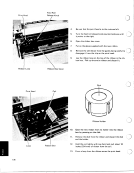
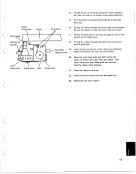
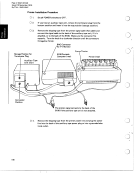
The rank of the result is the same as the rank of argument B. The length of the
first coordinate of the result is the same as the number of columns in argument B.
If argument A is a matrix, then the second coordinate of the result is the same
length as the second coordinate of argument A.
If argument B is a square matrix and argument A is a vector, then the result is
the solution to the set of linear equations with coefficient matrix B and right-hand
sides A:
If argument B is a square matrix and argument A is a matrix, then the columns of the
result are the solution to the sets of linear equations with coefficient matrix B and
right-hand sides equal to the columns of A:
At”:? 2026 lb v 6
B+2 2p3 5 1. 2
A
26 16
96
B
35
:L 2
ARB
7 2
1 2
If argument B is rectangular, then the result is the least squares solution to one or
more sets of linear equations:
Y.
- 1.
first coordinate of the result is the same as the number of columns in argument B.
If argument A is a matrix, then the second coordinate of the result is the same
length as the second coordinate of argument A.
If argument B is a square matrix and argument A is a vector, then the result is
the solution to the set of linear equations with coefficient matrix B and right-hand
sides A:
If argument B is a square matrix and argument A is a matrix, then the columns of the
result are the solution to the sets of linear equations with coefficient matrix B and
right-hand sides equal to the columns of A:
At”:? 2026 lb v 6
B+2 2p3 5 1. 2
A
26 16
96
B
35
:L 2
ARB
7 2
1 2
If argument B is rectangular, then the result is the least squares solution to one or
more sets of linear equations:
Y.
- 1.