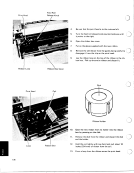
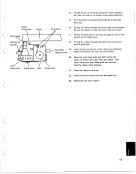
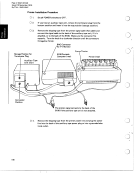
In Process
When the system is processing input, generally the display screen is blank and the
IN PROCESS light is on. After the input is processed, the light goes off, the out-
put and flashing cursor are displayed, and the system waits for input.
Notes:
1. For some expressions or user-defined functions (see Chapter 51, output is
generated before the expression or function has completed execution. In such
cases, even though the system is still processing data, the IN PROCESS light
goes off and the output is displayed. The flashing cursor is again displayed
wheD the system has finished processing the input (the expression or function
has completed execution).
brightness control before calling your service representative.
2. If the display screen is blank and the IN PROCESS light is off, check the
10
-
-.
.
I I
When the system is processing input, generally the display screen is blank and the
IN PROCESS light is on. After the input is processed, the light goes off, the out-
put and flashing cursor are displayed, and the system waits for input.
Notes:
1. For some expressions or user-defined functions (see Chapter 51, output is
generated before the expression or function has completed execution. In such
cases, even though the system is still processing data, the IN PROCESS light
goes off and the output is displayed. The flashing cursor is again displayed
wheD the system has finished processing the input (the expression or function
has completed execution).
brightness control before calling your service representative.
2. If the display screen is blank and the IN PROCESS light is off, check the
10
-
-.
.
I I