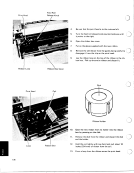
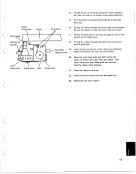
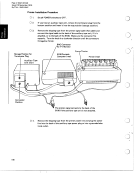
If B is the sine of an angle, then OOB yields the cosine of the same angle, and con-
versely, if B
is the cosine, OOB yields the sine. Suppose you wanted the sine of
30°, which is equivalent to pi divided by 6:
c. 1 (3 ( C) .:- b 1
B
0 C) B
0,:: Sine of 30'
0 I I36651334 Cosine of 30'
19 4- 2 C) ( C) + 6 1
IEC
I) I:] B
0 8 t36c',03~
0 #!54 Sine of 30'
Cosine of 30'
If one argument is a scalar or a single-element array, the shape of the result is the
same as that of the other argument. The single element is applied to every element
of the multielement array:
versely, if B
is the cosine, OOB yields the sine. Suppose you wanted the sine of
30°, which is equivalent to pi divided by 6:
c. 1 (3 ( C) .:- b 1
B
0 C) B
0,:: Sine of 30'
0 I I36651334 Cosine of 30'
19 4- 2 C) ( C) + 6 1
IEC
I) I:] B
0 8 t36c',03~
0 #!54 Sine of 30'
Cosine of 30'
If one argument is a scalar or a single-element array, the shape of the result is the
same as that of the other argument. The single element is applied to every element
of the multielement array: