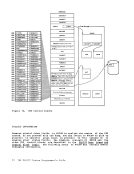
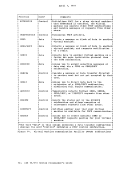
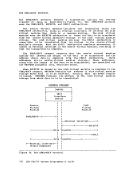
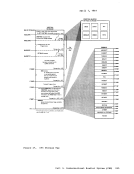
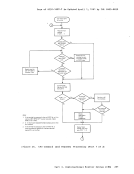
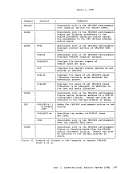
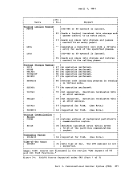
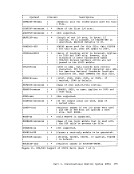
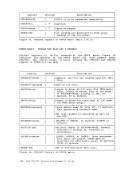
Page of GC20-1807-7 As Updated April 1, 1981 by TNL GN25-0829
TheSTCP command may be used to alter shared When the STep command is used to alter shared segments, the change is reflected to all
users of the shared segments; the altered shared system is not assigned
to the user issuing theSTCP command. Whenever the STCP command is
issued for a shared segment, storage is updated and the page that
changed is written to the paging volume, thus reflecting the change to
allusers of the shared segment. VIRTUAL MACHINE OPERATION If you issue a STORE, ADSTOP, or TRACE command that alters a storage
location within a shared segment,you receive the following message: DMKVMA181E SHARED COpy SYSTEM name REPLACED WITH NON-SHARED COpy Execution continues in your virtual machine; however, you are now
executing your own copy of the shared system in nonshared mode. The
nonshared system you are executing includes the change you just made;
all other users of the shared system continue to execute in shared mode
and are not affected by your change.
If you alter a shared page by any means other than the TRACE,ADSTOP, or STORE command, you receive the following message: DMKVMA456W CP ENTERED; name SHARED PAGE hexloc ALTERED You must enter the BEGIN command to continue execution. The altered
page will be returned to free storage by CP, and you may continue with
an unaltered system in shared mode.
If you issue anSTCP command that alters the storage of a shared
segment, storage is altered and the page altered is written to the
paging volume. All users, including you, remain in shared mode and the
change becomes part of the shared system. If operations overlap and you
issue aSTCP command for a shared page that is about to be assigned to a
particular user as nonshared (because he just altered it), you receive
the following message:DMKCDS161E SHARED PAGE hexloc ALTERED BY userid You should check that you issued the STCP command correctly and then
wait until the fresh copy of the saved system is loaded before reissuing
theSTCP command.
In attached processor systems it is invalid to issue theSTep command
to a shared segment. TheSTORE function is not performed, and the user DMKCDS004E INVALID HEXLOC - xxxxxx
142IBM VM/370 System programmer's Guide
The
users of the shared segments; the altered shared system is not assigned
to the user issuing the
issued for a shared segment, storage is updated and the page that
changed is written to the paging volume, thus reflecting the change to
all
location within a shared segment,
executing your own copy of the shared system in nonshared mode. The
nonshared system you are executing includes the change you just made;
all other users of the shared system continue to execute in shared mode
and are not affected by your change.
If you alter a shared page by any means other than the TRACE,
page will be returned to free storage by CP, and you may continue with
an unaltered system in shared mode.
If you issue an
segment, storage is altered and the page altered is written to the
paging volume. All users, including you, remain in shared mode and the
change becomes part of the shared system. If operations overlap and you
issue a
particular user as nonshared (because he just altered it), you receive
the following message:
wait until the fresh copy of the saved system is loaded before reissuing
the
In attached processor systems it is invalid to issue the
to a shared segment. The
142