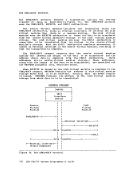
Appendix A: System/370 Information Control Registers
The control registers are used to maintain and manipulate
information that resides outside thePSi. There are sixteen
registers for control purposes. The control registers are not
addressable storage.
control
32-bit
part ofAt the time the registers are
for exceptions, such as invalid segment-size or page-size code or an
address designating an unavailable or a protected location. The
validity of the information is checked and the errors, if any, indicated
at the time the information is used.
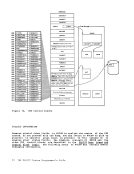
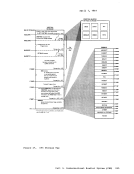
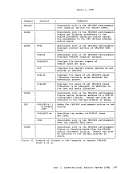
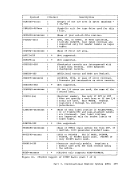
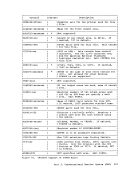
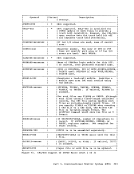
Figure 45 is a summary of the control register allocation and Figure
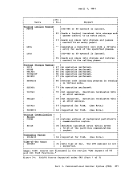
46 lists the facility associated with each control register.
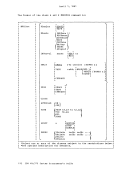
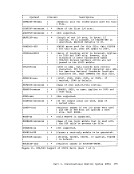
Figure 47 is a description of the EC (Extended Control)PSi. 32 bits -----------------------------) I OISYSTEM CONTROL ITRANSL. CONTROLI EXTERNAL-INTERRUPTION MASKS 1----------------------------------------------------------------- 1ISEGM-TBL LENGTHI SEGMENT-TABLE-ORIGIN-ADDRESSI I 21 CHANNEL MASKS 3
4
5
6
7
8
9PER EVENT MASKSI I 101 I 111 HARDWARE ASSIST CONTROLS MONITOR MASKS PER GR ALTERATION MASKS PER STARTING ADDRESS PER ENDING ADtRESS 1---------------------------------------------------------------- 121 I '"'l '- 1..)1 I 141 ERROR-RECOVERY CONTROL & MASKSI I 151 MCEL ADDRESS Figure 45. Control Register Allocation
Appendix A:System/370 Information 345
The control registers are used to maintain and manipulate
information that resides outside the
registers for control purposes. The control registers are not
addressable storage.
control
32-bit
part of
for exceptions, such as invalid segment-size or page-size code or an
address designating an unavailable or a protected location. The
validity of the information is checked and the errors, if any, indicated
at the time the information is used.
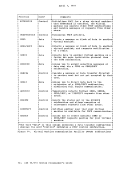
Figure 45 is a summary of the control register allocation and Figure
46 lists the facility associated with each control register.
Figure 47 is a description of the EC (Extended Control)
4
5
6
7
8
9
Appendix A: