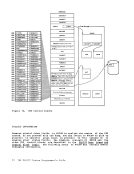
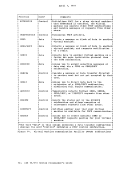
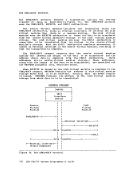
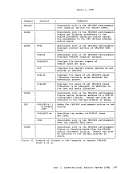
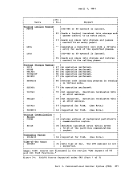
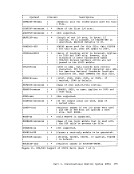
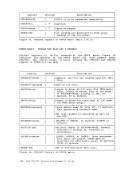
Asynchronous MSS Mount Processing When an MSS volume mount is required to satisfy a LINK or ATTACH command
or anMDISK or OED directory statement, CP returns control to the
virtual machine as soon asMSC accepts the mount request. The virtual
machine may continue to execute before thevirtual device specified en
theMDISK, OED, LINK, or ATTACH is available.
The reasons for asynchronousMSS mount processing are the relatively
long time required to complete the mount, and the chance that an errcr
may occur in theMSS after the mount order is accepted. The virtual
device to be mountedmay not be vital to the specific task to be
accomplished. Also, if an error occurs in theMSS (such as a permanent
read error on a cartridge) after the mount is accepted, the errcr
indication is passed from theMSC to the virtual machine. VM/370 cannot
determine that an error has occurred and that the mount will net
complete. If the virtual machine were not dispatchableuntil the mount completed, it would be locked out until the MSS error was corrected. With asynchronous mount processing, the virtual machine has the
flexibility to either continue processing without the affected virtual
device, or wait until theMSS mount completes. If the virtual machine
issues anSIO instruction to a virtual device that is defined on the
volume being mounted,VM/370 will queue the I/O request until the mount
completes. The virtual machine will be markedI/O wait nondispatchable
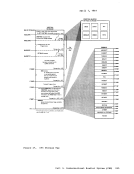
until the mount completes and theSIO is started. I VM/370 Processing of MSS Cylinder Faults VM/370 supports 3330V cylinder fault processing in two ways: real
channel programs directed to3330Vs are constructed so that cylinder
faults can be recognized and the channel program restarted; and the
attention interruption (indicating that the cylinder fault has been
satisfied) is recognized and any I/O for that device restarted.When the VM/370 processor issues a seek CCW to a 3330V device, the
staging adapter must translate the seek argument to the correct cylinder
of staging space. If the cylinder referenced in the seek is staged,
then theSIO is passed to the associated staging DASD drive. If the
referenced cylinder is not staged, the staging adapter initiates
cylinder fault processing. The staging adapter first passes a cylinder
fault indication to theMSC, requesting the cylinder of data to be
staged. It then returns a status modifier to the channel in response to
the seek, which causes the channel to skip oneCCW in its CCW fetch
processing. That is, the channel doesnQt fetch the next CCW after the
seek.
As a result of the cylinder fault, theMSC allocates staging space
for the requested data and causes it to bestaged. The staging adapter
then generates a channel end/device end interruption to indicate that
the cylinder has been staged.
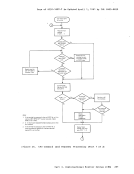
It is possible in error situations that the attention interruptionmay not be received. Each time an I/O request is queued by VM/370 as a
result of a cylinder fault, a timer is set. If the timer expires before
the interruption is received, a message(DMKSSS074I) is written to the VM/370 system operator and the request is retried. Part 2. Control Program (CP) 173
or an
virtual machine as soon as
machine may continue to execute before the
the
The reasons for asynchronous
long time required to complete the mount, and the chance that an errcr
may occur in the
device to be mounted
accomplished. Also, if an error occurs in the
read error on a cartridge) after the mount is accepted, the errcr
indication is passed from the
determine that an error has occurred and that the mount will net
complete. If the virtual machine were not dispatchable
flexibility to either continue processing without the affected virtual
device, or wait until the
issues an
volume being mounted,
completes. The virtual machine will be marked
until the mount completes and the
channel programs directed to
faults can be recognized and the channel program restarted; and the
attention interruption (indicating that the cylinder fault has been
satisfied) is recognized and any I/O for that device restarted.
staging adapter must translate the seek argument to the correct cylinder
of staging space. If the cylinder referenced in the seek is staged,
then the
referenced cylinder is not staged, the staging adapter initiates
cylinder fault processing. The staging adapter first passes a cylinder
fault indication to the
staged. It then returns a status modifier to the channel in response to
the seek, which causes the channel to skip one
processing. That is, the channel does
seek.
As a result of the cylinder fault, the
for the requested data and causes it to be
then generates a channel end/device end interruption to indicate that
the cylinder has been staged.
It is possible in error situations that the attention interruption
result of a cylinder fault, a timer is set. If the timer expires before
the interruption is received, a message