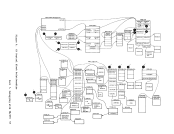
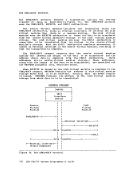
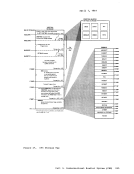
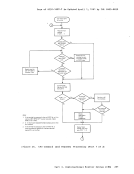
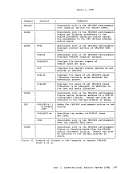
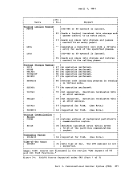
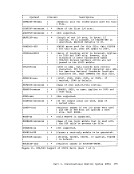
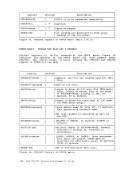
Auxiliary Directories When a disk is accessed, each module that fits the description specified
on theACCESS command is included in the resident directory. An
auxiliary directory is an extension of the resident directory and
contains the name and location of certainCMS modules that are not
included in the resident directory. These modules, if added to the
resident directory, would significantly increase its size, thus
increasing the search time and storage requirements. An auxiliary
directory can reference modules that reside on the system(S) disk; or,
if the proper linkage isprovided, reference modules that reside on any
other read-onlyCMS disk. To take advantage of the saving in search
time and storage, modules that are referenced via an auxiliary directory
should never be in the resident directory. The disk on which these
modules reside should be accessed in a way that excludes these mOdules.
How to Add an Auxiliary Directory
To add an auxiliary directory toeMS, the system programmer must
generate the directory, initialize it, and establish the proper linkage.Only when all three tasks are completed, can a module described in an
auxiliary directory be properly located.
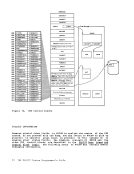
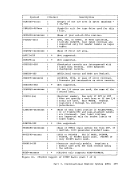
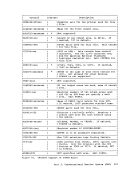
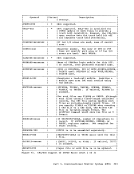
GENERATIONOF THE AUXILIARY DIRECTORY An auxiliary directory TEXT deck is generated by assembling a set cf DMSFST macros, one for each module name. The format of the DMSFST macro
is:DMSFST L filename ( (filename r , ; , filetype I) I L .J