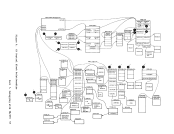
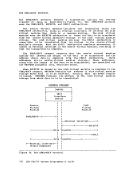
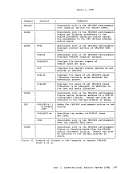
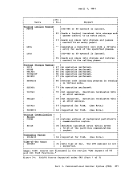
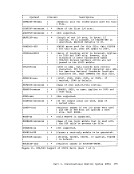
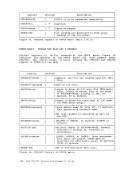
such a manner that multiple computing systems appear to exist. Each
"virtual" computing system, or virtual machine, is the functional
equivalent of an IBM
in the
counterparts of the components of a real
1
s console
is controlling the work flow of the virtual machine.
The virtual machines
techniques.
execution in another.
operate
the idle
concurrently
time of one
via multiprogramming
virtual machine with
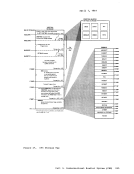
Each virtual machine is managed at two levels. The work to be done
by the virtual machine is scheduled and controlled
virtual machines is managed by the Control Program.
processor mode. For a description of the additional processing performed
when in attached processor mode, see
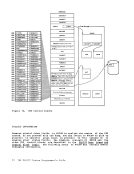
A virtual machine is created for a user when he logs on
basis of information stored in his
for each user identification includes a list of the virtual input/output
devices associated with the particular virtual machine.
Additional information
class, accounting data,
dispatching priority, and
as extended control mode.
about the virtual machine is kept in the
Included are the
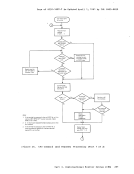
The Control Program supervises the execution of virtual machines by
(1) permitting only problem state execution except in its own routines,
and (2) receiving control after all real computing system interrupts.
current program status word of the issuing virtual machine indicates a
virtual supervisor state; if the virtual machine is executing in
virtual problem state, the attemFt to execute the privileged instruction
is reflected to the virtual machine as a program interrupt. All virtual
machine interrupts (including those caused by attempting privileged
instructions) are first handled by
machine if an analogous interrupt would have occurred on a real machine.