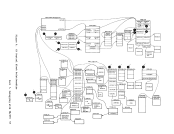
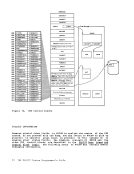
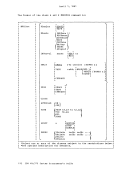
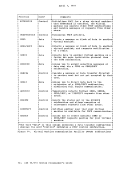
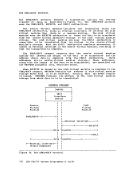
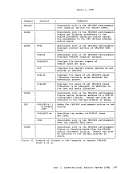
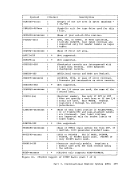
To provide for the metering of the flow of individual data streams, a
Function Control Sequence (FCS) is added to each transmission block.
Thepes is a sequence of bits, some of which represent a particular transmission stream. The receiver of several data streams can
temporarily stop the transmission of a particular streamby setting the
correspondingFCS bit off in the next transmission to the sender of that
stream. The stream can subsequently be resumedby setting the bit on. However, since only single data streams are supported, RSCS does not
support this metering capability. If bit one of theFCS (wait-a-bit) is
on, or if bits 4, 9, or 15 (print, console, punch stream identifiers)
are off, transmission will be suspended. Thus, the bit pattern ofX'SSC1' represents the m1n1mum acceptable FCS configuration for
transmission to be continued.
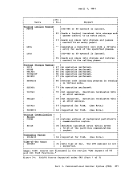
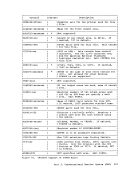
Finally, for error detection and correction purposes, a Block Control
Byte(BCB) is added as the first character of each block transmitted.
The BCB, inaddition to control inforaation, contains a hexadecimal
block sequence count. This count is maintained and verifiedby both the
sending and receiving systems to exercise a positive control over lost
or duplicated transmission blocks.
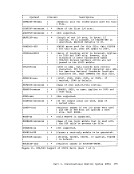
In addition to the normal binary synchronous text control characters(STX, ETB, etc.), MULTI-LEAVING uses two of the ESC control characters, ACKO and NAK. ACKO is used as a "filler" by all systems to maintain
coamunications when data is not available for transmission. NAK is used
as the only negative response and indicates that the previous
transmission was not successfully received.MULTI-LEAVING Control Specification
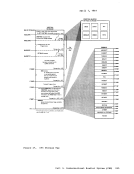
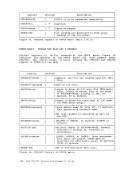
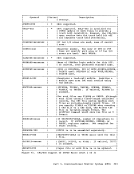
This section describes the bit-by-bit definitions of the variousMULTI-LEAVING control fields and includes notes concerning their MULTI-LEAVING 351
Function Control Sequence (FCS) is added to each transmission block.
The
temporarily stop the transmission of a particular stream
corresponding
stream. The stream can subsequently be resumed
support this metering capability. If bit one of the
on, or if bits 4, 9, or 15 (print, console, punch stream identifiers)
are off, transmission will be suspended. Thus, the bit pattern of
transmission to be continued.
Finally, for error detection and correction purposes, a Block Control
Byte
The BCB, in
block sequence count. This count is maintained and verified
sending and receiving systems to exercise a positive control over lost
or duplicated transmission blocks.
In addition to the normal binary synchronous text control characters
coamunications when data is not available for transmission. NAK is used
as the only negative response and indicates that the previous
transmission was not successfully received.
This section describes the bit-by-bit definitions of the various