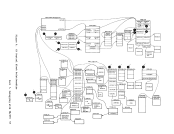
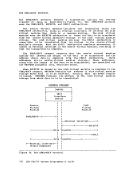
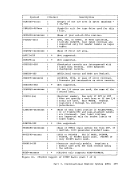
the virtual interval timer to be updated during virtual wait state as
well.
reflects virtual processor time and virtual wait time, but not cp
instruction execution. The more services a virtual machine requires
from
interval timer and the actual time used by and for the virtual machine.
The larger the
actual elapsed (wall clock)
A virtual machine must have the
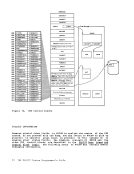
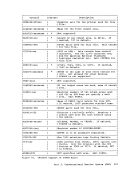
The processor timer is supported in a virtual machine in
same way as is the interval timer. That is, the processor timer in a
virtual machine records only virtual processor time, and it is updated
when the virtual machine passes control back to
all actual elapsed time except
privileged instruction execution, for that virtual machine.
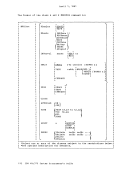
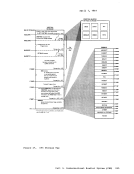
The method of sampling the value in the processor timer causes it to
appear to a virtual machine to be updated more often than an interval
timer. The privileged instructions
processor timer and to store it in a doubleword location of virtual
storage.
timer by issuing a
rrivileged instruction, and updates the time. The act of sampling the
processor timer from a virtual machine causes it to
date.
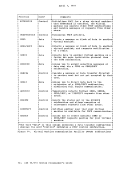
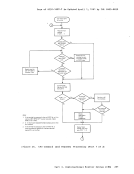
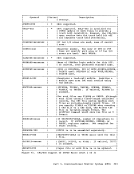
virtual machine. The
real TaD clock for each processor, and all virtual machines can
interrogate the real TaD clock. The Store Clock
nonprivileged; any virtual machine can execute it to store the current
value of the
from a virtual machine, but
and does not actually
only true source of actual elapsed time information for a virtual
machine. The base value for the TaD clock in
using the procedure described in the