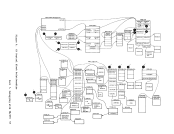
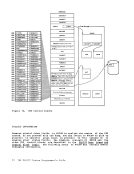
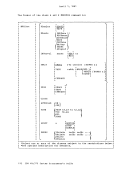
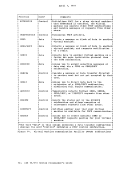
April 1, 1981
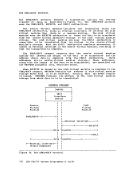
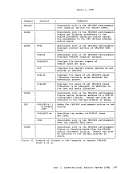
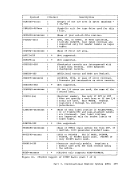
FLCLB
destroyed.
FLHC
and user high-storage chains.
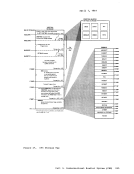
and high storage
a full 4K page available on the chain. This flag may be set
even if
contains the one-byte storage key assigned to storage on this
chain.
contains the one-byte FREETAB table code for storage on this
chain.
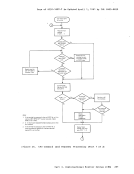
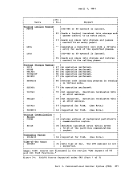
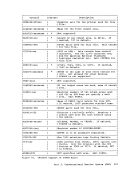
following steps are taken in an attempt to satisfy the request. As soon
as one of the following steps succeeds, then user free storage
allocation processing terminates.
1. search the
2.
size.
3. Extend high storage user storage downward into the user program
area, modifying
4. For a variable request, put all available storage in the user
the largest block available on either the high storage user chain
or the
satisfactory unless it is larger than the minimum requested size.
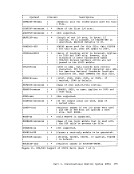
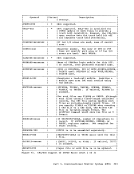
in an attempt to satisfy the request, until one succeeds:
1.
size.
2. Get
available, and put them on the low storage nucleus chain.
3.
size.
4. Get
available, and put them on the high storage nucleus chain.