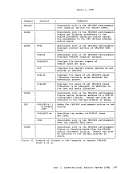
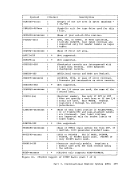
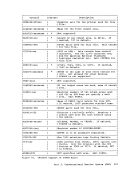
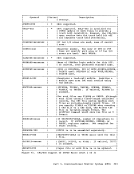
April 1, 1981 COMMANDS THAT ALTER THE CONTENTS OF STORAGE You can use the STORE, STCP, and ZAP commands to alter the contents of storage: Use the STORE command to alter the contents of specified registers and
locations in virtual machine storage. The contents of the following can
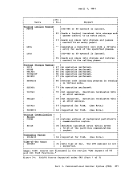
be altered:e Virtual machine storaqe locations (first-level virtual storage only) • General registers • Floating-point registers • Control registers (if available) • Program Status Word The STORE STATUS command can save certain information contained in low
storaqe.When debugging, you may find it advantageous to alter storage,
registers, or thePSW and then continue execution. This is a good
procedure for testing a proposed change. Also, you can make a temporary
correction and then continue to ensure that the rest of execution is
trouble-free. A procedure for using theSTORE STATUS command when
debugging is as follows:• Issue the STORE STATUS command before entering a routine you wish to
debug.• When execution stops (because an address stop was reached or because
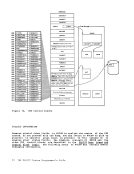
of failure), display the extended logout area. This area contains
the status that was stored before entering the routine.• Issue STORE STATUS again and display the extended logout area again. You now have the status information before and after the failure.
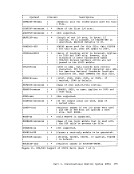
This information should help you solve theproblemc Use the STCP command to alter the contents of real storage.
command cannot alter the realPSW or real registers.
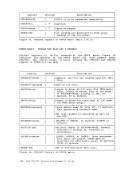
TheSTCP ZAP command to modify or dump MODULE, LOADLIB, or TITLIB files. ZA-Pcan be used to modify either fixed-or variable-length r.ODULE files.
It is for usebV system support personnel only. Part 1. Debugging with VM/370 41
locations in virtual machine storage. The contents of the following can
be altered:
storaqe.
registers, or the
procedure for testing a proposed change. Also, you can make a temporary
correction and then continue to ensure that the rest of execution is
trouble-free. A procedure for using the
debugging is as follows:
debug.
of failure), display the extended logout area. This area contains
the status that was stored before entering the routine.
This information should help you solve the
command cannot alter the real
The
It is for use