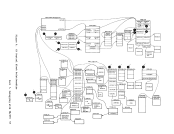
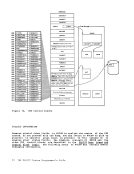
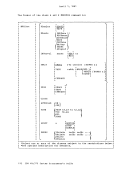
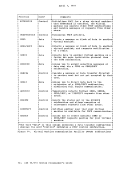
April 1, 1981 ACCESS METHOD SUPPORT The manipulation of data is governed by an access method. To facilitate
the execution ofOS Code under eMS, the processing program must see data
asOS would present it. For instance, when the processors expect an
access method to acquire input source cards sequentially,CMS invokes specially written routines that simulate the OS sequential access method and pass data to the processors in the format that the OS access methods
would have produced. Therefore, data appears in storage as if it had
been manipulated using anOS access method. For example, block
descriptor words(BOW), buffer pool management, and variable records are
updated in storage as if anOS access method had processed the data.
The actual writinq to and reading from theI/O device is handled by CMS file manaqement. Note that the character string X'61FFFF61' is eMS as an end of file indicator.
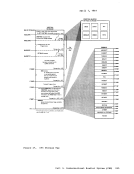
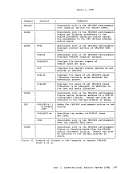
The essential work of the volume table of contents(VTOe) and the
data set control block(OSCB) is done in eMS by a master file directory (MFO) which updates the disk contents, and a file status table (FST) (one for each data file). All disks are formatted in physical blocks of 800 bytes. eMS continues to update the OS format, within its own format, on the
block and record descriptor words(BOW and ROW) are written along with
the data. If a data set consists of blocked records, the data is
written to, and read from, theI/O device in physical blocks, rather
thanloqical records. eMS also simulates the specific methods of
manipulating data sets.
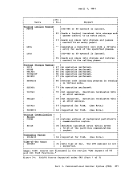
To accomplish this simulation,CMS supports certain essential macros
for the following access methods:• BDAM • BPAM • BSAM/QSAM • VSAM (direct) --identifying a record by a key or by its
relative position within the data set.
(partitioned) --seeking a named member within data set.
(sequential) --accessing a record in a sequence in
relation to preceding or following records.
(direct or sequential) --accessing a record sequentially
or directly by key or address.CMS support of OS VSAM files is based on DOS/VS Access Method Services and Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM). Therefore, the OS user is restricted to those
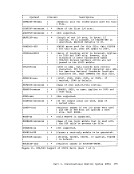
functions available under"DOS/VS Access Method Services." See the section "eMS Support for as and DOS VSAM Functions" for details. CMS also updates those portions of the OS control blocks that are
needed by the as simulation routines to support a program durinq
execution. Most of the simulated supervisoryOS control blocks are
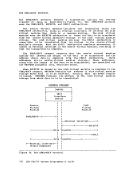
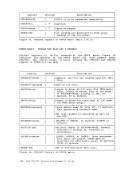
contained in the following twoeMS control blocks: CMSCVT simulates the communication vector table. Location 16 contains
the address of theCVT control section.
278 IBMVM/370 System Programmer's Guide
the execution of
as
access method to acquire input source cards sequentially,
would have produced. Therefore, data appears in storage as if it had
been manipulated using an
descriptor words
updated in storage as if an
The actual writinq to and reading from the
The essential work of the volume table of contents
data set control block
block and record descriptor words
the data. If a data set consists of blocked records, the data is
written to, and read from, the
than
manipulating data sets.
To accomplish this simulation,
for the following access methods:
relative position within the data set.
(partitioned) --seeking a named member within data set.
(sequential) --accessing a record in a sequence in
relation to preceding or following records.
(direct or sequential) --accessing a record sequentially
or directly by key or address.
functions available under
needed by the as simulation routines to support a program durinq
execution. Most of the simulated supervisory
contained in the following two
the address of the
278 IBM