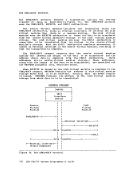
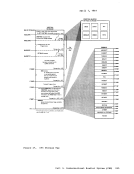
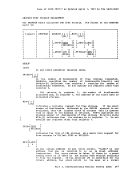
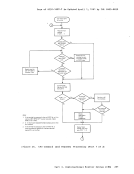
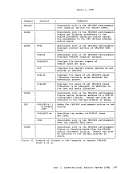
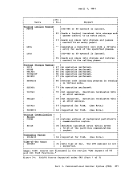
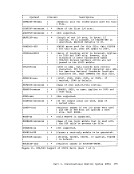
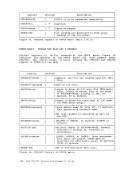
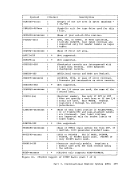
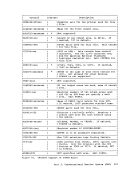
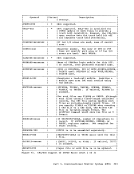
Inactive pages are kept on a direct access storage device. If an
inactive page bas been changed at some time during virtual machine
execution,CP assigns it to a paging device, selecting the fastest such device with available space. If the page has not changed, it remains
allocated in its original direct access location and is paged into real
storaqe from there the next time the virtual machine references that
page.- A virtual machine program can use the DIAGNOSE instruction to
tellCP that the information from specific pages of virtual storage is
no longer needed;CP then releases the areas of the paging devices which
were assigned to hold the specified pages.Paging is done on demand by CP. This means that a page of virtual
storage is not read (paged)from the paging device to a real storage
block until it is actually needed for virtual machine execution.CP makes no attempt to anticipate what pages might te required by a virtual
.achine.While a paging operation is performed for one virtual machine,
another virtual machine can be executing. Any paging operation
initiated byCP is transparent to the virtual machine.
If the virtual machine is executing in extended control mode with
translate on, then two additional sets of segment and page tables are
kept. The virtual machine operating system is responsible for mapping
the virtual storage created by it to the storage of the virtual machine.
CP uses this set of tables and the page and segment tables created for
the virtual machine at logon time to build shadow page tables for the
virtual machine. These shadow tablesBap the virtual storage created by
the virtual machine operating system to the storage of the real
computing system. The tables created by the virtualmachine operating
system may describe any page and segment size permissible in theIBM System/370. YM/370 provides both fetch and store protection for real storage. The
contents of real storage are protected from destruction ormisuse caused
by erroneous or unauthorized storing or fetching by the program.
Storage is protected from improper storing or from both improper storing
andfetching, but not from improper fetching alone. When protection applies to a storage access, the key in storage is
compared with the protection key associated with the request for storage
access. A store or fetch is permitted only when the key in storagematches the protection key. When a store access is prohibited because of Frotection, the contents
of the protected location remain unchanged.On fetching, the protected
information is not loaded into an addressable register, moved to another
storage location, or provided to an I/O device.When a processor access is prohibited because of protection, the
operation is suppressed or terminated, and a program interruption for a
protection exception takes place.When a channel access is prohibited,
a protection-check condition is indicated in the channel status word(CSW) stored as a result of the operation. Part 2. Control program (CP) 77
inactive page bas been changed at some time during virtual machine
execution,
allocated in its original direct access location and is paged into real
storaqe from there the next time the virtual machine references that
page.
tell
no longer needed;
were assigned to hold the specified pages.
storage is not read (paged)
block until it is actually needed for virtual machine execution.
.achine.
another virtual machine can be executing. Any paging operation
initiated by
If the virtual machine is executing in extended control mode with
translate on, then two additional sets of segment and page tables are
kept. The virtual machine operating system is responsible for mapping
the virtual storage created by it to the storage of the virtual machine.
CP uses this set of tables and the page and segment tables created for
the virtual machine at logon time to build shadow page tables for the
virtual machine. These shadow tables
the virtual machine operating system to the storage of the real
computing system. The tables created by the virtual
system may describe any page and segment size permissible in the
contents of real storage are protected from destruction or
by erroneous or unauthorized storing or fetching by the program.
Storage is protected from improper storing or from both improper storing
and
compared with the protection key associated with the request for storage
access. A store or fetch is permitted only when the key in storage
of the protected location remain unchanged.
information is not loaded into an addressable register, moved to another
storage location, or provided to an I/O device.
operation is suppressed or terminated, and a program interruption for a
protection exception takes place.
a protection-check condition is indicated in the channel status word