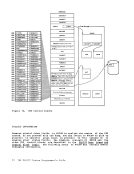
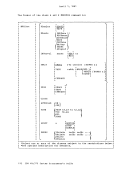
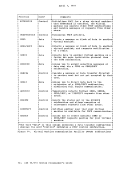
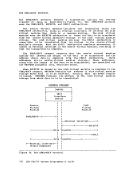
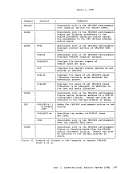
label INIT1 IBIT2
CHECK
is any valid Assembler language label.
invokes the first free storage initialization routine, so
that free storage requests can be made to access
requests may be made. After INIT1 has been invoked, free
storage requests may be made, but these are subject to
the following restraints until the second free storage
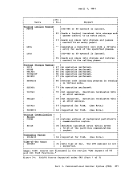
management initialization routine has been invoked:• All requests for USER type storage are changed to
requests forNUCLEUS type storage. • Error checking is limited before initialization is
release a block that was never allocated.• All requests that are satisfied in high storage must
be of a temporary nature, since all storage allocated1n high storage is released when the second free
storage initialization routine is invoked.When CP's saved system facility is used, the CMS system
is saved at the point just after the A-Disk has been made
accessible. It is necessary forDMSFRE to be used before
the size of virtual storage is known, since the saved
system can be used on any size virtual machine. Thus,
the first initialization routine initializesDMSFRE so
that limited functions can be requested, while the second
initialization routine performs the initialization
necessary to allow the full functions ofDMSFRE to be
exercised.
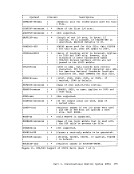
invokes the second initialization routine. This routine
is invoked after the size of virtual storage is known,
and it performs initialization necessary to allow all the
functions ofDMSFRE to be used. The second
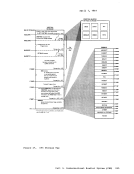
initialization routineperforms the following steps: • Releases all storage that has been allocated in the
high storage area.• Allocates the FREETAB free storage table. This table
contains one byte for each 4K page of virtual storage,
and so cannot be allocated until the size of virtual
storage is known.• The FREETAB table is initialized, and all storage
protection keys are initialized.• All completely unallocated 4K pages on the low storage
nucleus free storage chain areremoved to the user
chain. Any other necessary operations are performed.
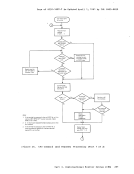
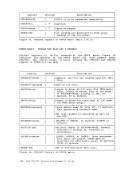
invokes a routine that checks all free storage chains for
consistency and correctness. Thus, it checks to see
whether or not any free storage pointers have been
destroyed. This option can be used at any time for
system debugging.Part 3. Conversational Monitor System (CMS) 253
CHECK
is any valid Assembler language label.
invokes the first free storage initialization routine, so
that free storage requests can be made to access
requests may be made. After INIT1 has been invoked, free
storage requests may be made, but these are subject to
the following restraints until the second free storage
management initialization routine has been invoked:
requests for
release a block that was never allocated.
be of a temporary nature, since all storage allocated
storage initialization routine is invoked.
is saved at the point just after the A-Disk has been made
accessible. It is necessary for
the size of virtual storage is known, since the saved
system can be used on any size virtual machine. Thus,
the first initialization routine initializes
that limited functions can be requested, while the second
initialization routine performs the initialization
necessary to allow the full functions of
exercised.
invokes the second initialization routine. This routine
is invoked after the size of virtual storage is known,
and it performs initialization necessary to allow all the
functions of
initialization routine
high storage area.
contains one byte for each 4K page of virtual storage,
and so cannot be allocated until the size of virtual
storage is known.
protection keys are initialized.
nucleus free storage chain are
chain. Any other necessary operations are performed.
invokes a routine that checks all free storage chains for
consistency and correctness. Thus, it checks to see
whether or not any free storage pointers have been
destroyed. This option can be used at any time for
system debugging.