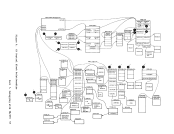
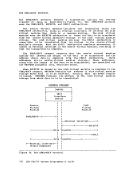
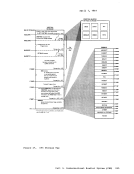
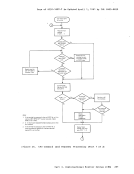
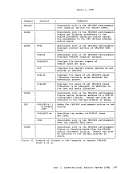
and are used to display real storage locations. The
the contents of real storage to your virtual printer. The
displays at your terminal the contents of real storage locations.
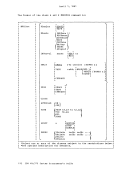
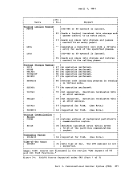
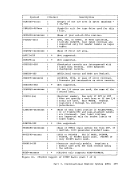
The class G
reader spool file.
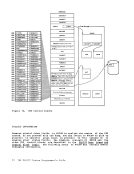
written by
section.
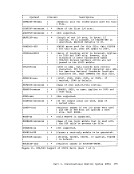
the
The
used to clear storage.
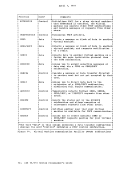
The functions of the
messages that may be useful while you are debugging.
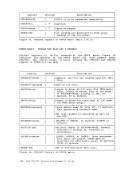
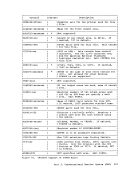
The
other users via the
whether you receive messages from
printer, or punch files to your virtual machine.
The
message flag. If the virtual machine has issued
(Authorize), this flag determines whether the virtual machine accepts or
rejects messages sent via the
messages are accepted.
The
from the system operator.
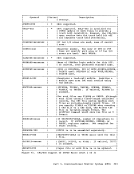
The
operand
message
specify
spooled
text, or both to be displayed at your terminal.
that no messages be displayed (except in the case where you have
your console output).
a t your terminal.
The
by the
the