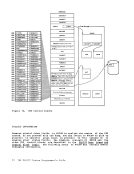
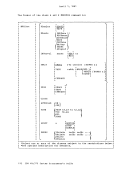
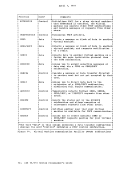
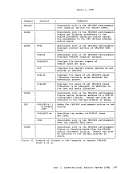
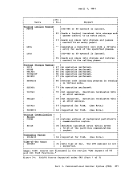
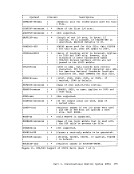
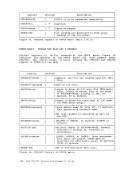
Using Processor Resources CP allocates the processor resource to virtual machines according to
their operating characteristics, priority, and the system resources
available.Virtual machines are dynamically categorized at the end of each time
slice as interactive or noninteractive, depending upon the frequency of
operations to or from either the virtual system console or a terminal
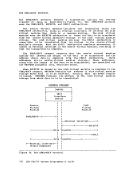
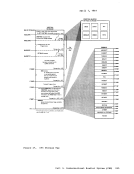
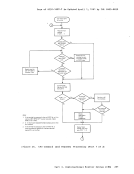
controlled by the virtual machine.Virtual machines are dispatched from one of two queues, called Queue
1 and Queue 2. In order to be dispatched from either queue, a virtualmachine must be considered executable (that is, not waiting for some
activity or forsome other system resource). Virtual machines are not
considered dispatchable if the virtual machine:• Enters a virtual wait state after an I/O operation has begun. • Is waiting for a page frame of real storage. • Is waiting for an I/O operation to be translated by CP and started. • Is waiting for CP to simulate its privileged instructions. • Is waiting for a CP console function to be performed.
Queue 1Virtual machines in Queue 1 (Q1) are considered conversational or
interactive users, and enter this queue when an interruptfrom a
terminal is reflected to the virtual machine.Users are considered fer
dispatching from this queue on a first-in-first-out(FIFO) basis. When a virtual machine uses more than a certain amount of processor time without entering a virtual wait state, that user is placed in Queue 2. Virtual machines are dropped from Q1 when they complete their time slice of processor usage, and are placed in an "eligible list". Virtual machines entering CP command mode are also dropped from Q1. When the
virtual machine becomes executable again (returns to execution mode) it
is placed at the bottom of Q1.
Queue 2Virtual machines in Queue 2 (Q2) are considered noninteractive users. Users are selected to enter Q2 from a list of eligible virtual machines
(the "eligible list"). The list of eligible virtual machines is sorted
on aFIFO basis within user priority (normally defined in the user
record in theVM/370 directory, but may be altered by the system
operator).
usually, a virtual machine is selected to enter Q2 only if its
"workingset" is not greater than the number of real page frames
available for allocation at the time. The working set of a virtual
machine is calculated and saved each time a user is dropped from Q2 and
is based on the number of virtual pages referred toby the virtual
machine during its stay in Q2, and the number of its virtual pages that
are resident in real storage at the time it is dropped from the queue.84 IBM VM/37C System ProgrammeL's Guide
their operating characteristics, priority, and the system resources
available.
slice as interactive or noninteractive, depending upon the frequency of
operations to or from either the virtual system console or a terminal
controlled by the virtual machine.
1 and Queue 2. In order to be dispatched from either queue, a virtual
activity or for
considered dispatchable if the virtual machine:
Queue 1
interactive users, and enter this queue when an interrupt
terminal is reflected to the virtual machine.
dispatching from this queue on a first-in-first-out
virtual machine becomes executable again (returns to execution mode) it
is placed at the bottom of Q1.
Queue 2
(the "eligible list"). The list of eligible virtual machines is sorted
on a
record in the
operator).
usually, a virtual machine is selected to enter Q2 only if its
"working
available for allocation at the time. The working set of a virtual
machine is calculated and saved each time a user is dropped from Q2 and
is based on the number of virtual pages referred to
machine during its stay in Q2, and the number of its virtual pages that
are resident in real storage at the time it is dropped from the queue.