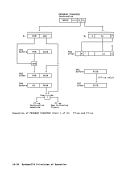
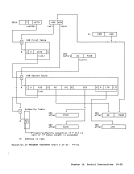
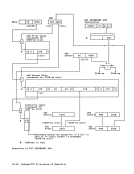
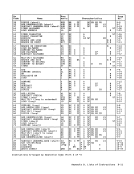
disabled for all interruptions at
the time of the reset. Except for
the operation of the interval timer
andCPU timer and for the possibil
ity of a machine-check interruption
occurring, allCPU activity can be stopped by placing the CPU in the
waitstate and by disabling it for I/O and external interruptions. To
avoid the possibility of causinga reset at the time that the interval
timer orCPU timer is being updated
or a machine-check interruption
occurs,the CPU must be in the stopped state.
2.CPU reset, initial CPU reset,
subsystem reset, program reset,
initial program reset, and clear
reset do not affectthe value and
state ofthe TOO clock.
3. The conditions under which theCPU enters the check-stop state are model-dependent and include
malfunctions that preclude the
completion ofthe current
operation. Hence, ifCPU reset,
initialCPU reset, program reset, or initial program reset is
executed while theCPU is in the
check-stop state, the contents of
thePSW, registers, and storage
locations, including the storage
keys andthe storage location
accessed at the time of the error,may have unpredictable values, and,
in some ca5es, the contentsmay still be in error after the check
stop state is cleared bythese resets. In this situation, a clear
resetis required to clear the
error.
4.Clear reset causes all bit posi
tions of the interval timer to be
cleared to zeros.Power-On Reset
The power-on-reset function fora compo
nent of the machine is performed as part
of the power-on sequence for that compo
nent.
The power-on sequences for theTOO clock, vector facility, main storage, expanded storage, and channels may be included as part of the CPU power-on scquence, or the power-on sequence for these units may be initiated separately.
The following sections describe the
power-on resets forthe CPU, TOD clock,
vector facility, main storage,expanded storage, and channels. See also Chapter 13, "Input/Output Operations," and the
appropriate System Library publication~ for channels, control units, and I/O devices. CPU Power-On Reset: The power-on reset causes initial CPU reset to be performed
and mayor may not causeI/O-system reset to be performed in the channels
connected to theCPU. The contents of
general registers and floating-point
registers normally are cleared tozeros, but in some models may be left unpre
dictable, with valid checking-block
code.TOO-Clock Power-On Reset: The power-on reset causes the va~of the TOO clock
tobe set to zero and causes the clock
toenter the not-set state.
Vector-FacilityPower-On Reset: The
power-on reset causes the registers ofthe vector facility (vector-status
register, vector-mask register, vector
activity count, and all vector
registers) to be cleared to zeros with
valid checking-block code.
Main-StoragePower-On Reset: For vola
tile main storage (one that does not
preserve its contents when power is off)
and for storage keys, power-on reset
causes valid checking-block code tobe placed in these fields. In most models, the contents are cleared to zeros, but,
in some models, the contents may be left
unpredictable except for the checking
block code. The contents of nonvolatile
main storage, includingthe checking
block code, remain unchanged.
Expanded-StoragePower-On Reset: The
contents ofthe expanded storage are cleared to zeros with valid checking
block code.Channel Power-On Reset: The channel pOL.Jer-on reset causes I/O-system reset
to be performed. (Seethe section "I/O-System Reset" in Chapter 13,
"Input/Output Operations.")
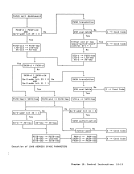
INITIALPROGRAM LOADING Initial program loading (IPL) provides a manual means for causing a program to be read from a designated device and for
initiating execution of that program.
Some models may provide additional
controls and lndications relating toIPl; this additional information is
specified inthe System library publica
tion forthe model. IPL is initiated manually by setting the
load-unit-address controls to designate
an input device and by subsequently
activating the load-clear or load-normal
key for a particularCPU. In the description which follows, the term "this CPU" refers to the CPU in the
configuration for whichthe load-clear
or load-normalkey was activated. Chapter 4. Control 4-35
the time of the reset. Except for
the operation of the interval timer
and
ity of a machine-check interruption
occurring, all
wait
avoid the possibility of causing
timer or
or a machine-check interruption
occurs,
2.
subsystem reset, program reset,
initial program reset, and clear
reset do not affect
state of
3. The conditions under which the
malfunctions that preclude the
completion of
operation. Hence, if
initial
executed while the
check-stop state, the contents of
the
locations, including the storage
keys and
accessed at the time of the error,
in some ca5es, the contents
stop state is cleared by
reset
error.
4.
tions of the interval timer to be
cleared to zeros.
The power-on-reset function for
nent of the machine is performed as part
of the power-on sequence for that compo
nent.
The power-on sequences for the
The following sections describe the
power-on resets for
vector facility, main storage,
appropriate System Library publication
and mayor may not cause
connected to the
general registers and floating-point
registers normally are cleared to
dictable, with valid checking-block
code.
to
to
Vector-Facility
power-on reset causes the registers of
register, vector-mask register, vector
activity count, and all vector
registers) to be cleared to zeros with
valid checking-block code.
Main-Storage
tile main storage (one that does not
preserve its contents when power is off)
and for storage keys, power-on reset
causes valid checking-block code to
in some models, the contents may be left
unpredictable except for the checking
block code. The contents of nonvolatile
main storage, including
block code, remain unchanged.
Expanded-Storage
contents of
block code.
to be performed. (See
"Input/Output Operations.")
INITIAL
initiating execution of that program.
Some models may provide additional
controls and lndications relating to
specified in
tion for
load-unit-address controls to designate
an input device and by subsequently
activating the load-clear or load-normal
key for a particular
configuration for which
or load-normal