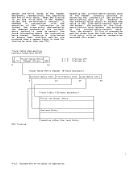
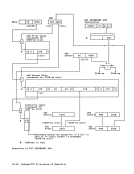
STD field is placed in both the PSTD and SSTD, bits 0-31 of control registers 1
and7, respectively. The contents of
the entire STD field are placed in the
appropriate control registers without
being inspected for validity.
Space-Switch-Event Control(X): Bit 31
of the segment-table designation is the
space-switch-event-control bit. When,
in PC-ss or PT-ss, this bit is one in
control register 1 either before or
after the execution of the PC-ss or
PT-ss,a program interruption for a space-switch event occurs after the
execution of the instructionis completed. When, in LOAD ADDRESS SPACE
PARAMETERS, this bit is one during
primary ASN translation, this factis indicated by the condition code.
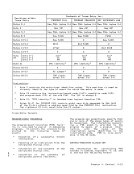
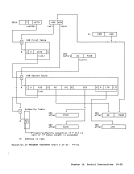
Linkage-Table Designation (LTD): Bits
96and 104-127 are used as a result of
primary ASN translation. The linkage
table-designationfield contains the
subsystem-linkage-control bit (V) (bit
96), the linkage-table origin (LTD)
(bits104-120), and the linkage-table
length (LTL) (bits 121-127). The
contents of the LTD field are placed in
control register 5as a result of prima
ry ASN translation.
Bits 1-7,30, 31, 60-63, and 97-103 of
the AST entry mustbe zeros; otherwise,
an ASH-translation-specification excep
tion is recognized as part of the
execution of the instruction using that
entry for ASN translation.
Programming Note
The unused portion of the STD field,
bits90-94 of the AST entry, which
corresponds to bits26-30 of the PSTD
and SSTD, shouldbe set to zeros. These
bits are reserved for future expansion,
and programs which place nonzero values
in these bit positions may not operate
compatibly on future machines.
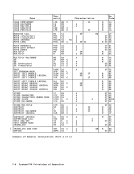
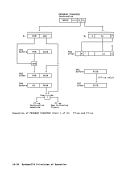
ASN-TRANSLATION PROCESS
This section describes the ASN
translation process as it is performed
during the execution of PROGRAM CALL
with space switching,PROGRAM TRANSFER
with space switching, and SETSECOHDARY ASH with space switching. ASH trans
lation forLOAD ADDRESS SPACE PARAMETERS
is the same, except that AFX-translation
and ASX-translation exceptions do not
occur; such situations are instead indi
cated by the condition code.
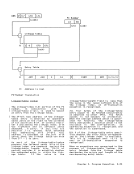
Translation of an ASN is performed by
means of two tables, an ASN first tableand an ASN second table, both of which
reside in main storage.
TheASH first index is used to select an entry from the ASN first table. This
entry designates the ASN second table to
be used.
TheASH second index is used to select
an entry from the ASN second table.
This entry contains the address-space
control parameters.
If the I bit is one in either the ASN
first-table entry or ASN-second-table
entry, the entryis invalid, and the
ASN-translation process cannot be
completed. An AFX-translation exception
or ASX-translation exception is recog
nized.Whenever access to main storage is made
during the ASN translation process forthe purpose of fetching an entry from an
ASN first table or ASN second table,
key-controlled protection does not
apply.
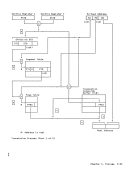
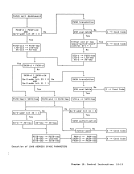
The ASN translation process is shown in
the figure "ASN Translation."
Chapter 3. Storage 3-15
and
the entire STD field are placed in the
appropriate control registers without
being inspected for validity.
Space-Switch-Event Control
of the segment-table designation is the
space-switch-event-control bit. When,
in PC-ss or PT-ss, this bit is one in
control register 1 either before or
after the execution of the PC-ss or
PT-ss,
execution of the instruction
PARAMETERS, this bit is one during
primary ASN translation, this fact
Linkage-Table Designation (LTD): Bits
96
primary ASN translation. The linkage
table-designation
subsystem-linkage-control bit (V) (bit
96), the linkage-table origin (LTD)
(bits
length (LTL) (bits 121-127). The
contents of the LTD field are placed in
control register 5
ry ASN translation.
Bits 1-7,
the AST entry must
an ASH-translation-specification excep
tion is recognized as part of the
execution of the instruction using that
entry for ASN translation.
Programming Note
The unused portion of the STD field,
bits
corresponds to bits
and SSTD, should
bits are reserved for future expansion,
and programs which place nonzero values
in these bit positions may not operate
compatibly on future machines.
ASN-TRANSLATION PROCESS
This section describes the ASN
translation process as it is performed
during the execution of PROGRAM CALL
with space switching,
with space switching, and SET
lation for
is the same, except that AFX-translation
and ASX-translation exceptions do not
occur; such situations are instead indi
cated by the condition code.
Translation of an ASN is performed by
means of two tables, an ASN first table
reside in main storage.
The
entry designates the ASN second table to
be used.
The
an entry from the ASN second table.
This entry contains the address-space
control parameters.
If the I bit is one in either the ASN
first-table entry or ASN-second-table
entry, the entry
ASN-translation process cannot be
completed. An AFX-translation exception
or ASX-translation exception is recog
nized.
during the ASN translation process for
ASN first table or ASN second table,
key-controlled protection does not
apply.
The ASN translation process is shown in
the figure "ASN Translation."
Chapter 3. Storage 3-15