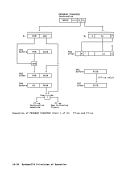
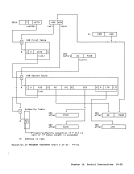
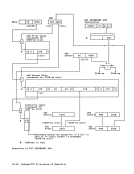
in START I/O and START I/O FAST
RELEASE1-2 in store accesses I-I in subchannel interruption-pending
state 1-2
completion
ofI/O operations 13-54
of instruction execution 5-9
of unit of operation5-10 conceptual sequence 5-24
as related to storage-operand
accesses 5-32
conclusion
of data transfer(I/O) 13-56
ofI/O operations 13-54
of instruction execution 5-8CONCS (CONNECT CHANNEL SET) instruction 10-4 concurrency of access for storage refer
ences 5-31
condition code 4-7
deferred (See deferred condition
code)
forI/O operations 13-12
inBC-mode PSW 4-8
inEC-mode PSW 4-7
summaryC-l tested by BRANCH ON CONDITION instruction 7-10 used for decision making 5-6
validity bit for 11-22
conditional-swapping facility 0-2
conditional swapping instructions(See COMPARE AND SWAP instruction, COMPARE DOUBLE AND SWAP instruction)
conditions for interruption (See inter
ruption)
configuration 2-2
of storage 3-5CONNECT CHANNEL SET (CONCS) instruction 10-4 connection of channels (See channel
set)
connective(See logical connective)
consistency (storage operand)5-30 examples A-44,A-47
console device 12-1
control 4-2as an I/O command 13-50 instructions 10-2 manual (See manual operation)
control register 2-4,4-8save areas 3-45
validity bit 11-23
control-register assignment4-10 (CRx.y indicates control register x,
bit position y)CRO.O: block-multiplexing-control bit
13-5,13-17,13-27CRO.1: SSM-suppression-control bit 6-25,10-46 CRO.2: TOD-clock-sync-control bit
4-24,4-27CRO.3: low-address-protection-control bit
3-9CRO.4: extraction-authority-control bit
5-17CRO.5: secondary-space-control bit
3-23,5-18CRO.7: storage-key exception-control bit 3-7,6-26 CRO.8-12: translation format 3-23 CRO.14: vector-control bit 4-11 CRO.16: malfunction-alert subclass-mask bit 6-13 CRO.17: emergency-signal subclass-mask bit
6-11CRO.18: external-call subclass-mask bit
6-12CRO.19: TOO-clock sync-check subclass-mask bit 6-13 CRO.20: clock-comparator subclass-mask bit 6-11 CRO.21: CPU-timer subclass-mask bit 6-11 CRO.22: service-signal subclass-mask bit
6-13CRO.24: interval-timer subclass-mask bit
6-12CRO.25: interrupt-key subclass-mask bit 6-12 CRO.26: external-signal subclass-mask bit
6-12CRl.0-7: primary segment-table length
(PSTL) 3-24CR1.8-25: primary segment-table origin (PSTO) 3-24 CR1.31: space-switch-event-control bit
3-24,6-25CR2.0-31: channel masks 6-14 CR3.0-15: PSW-key mask (PKM) 5-18 CR3.16-31: secondary ASN (SASN) 3-13,5-14 CR4.0-15: authorization index (AX)
3-17,5-18
CR4.16-31:
primary ASN (PASN) 3-13,5-14CR5.0: subsystem-linkage-control bit
5-18,5-21CR5.8-24: linkage-table origin (LTO) 5-21 CR5.25-31: linkage-table length (LTL) 5-21 CR7.0-7: secondary segment-table length
(SSTL) 3-24CR7.8-25: secondary segment-table origin (SSTO) 3-24 CR8.16-31: monitor-mask bits 6-21 CR9.0: Index X-5
RELEASE
state 1-2
completion
of
of instruction execution 5-9
of unit of operation
as related to storage-operand
accesses 5-32
conclusion
of data transfer
of
of instruction execution 5-8
ences 5-31
condition code 4-7
deferred (See deferred condition
code)
for
in
in
summary
validity bit for 11-22
conditional-swapping facility 0-2
conditional swapping instructions
conditions for interruption (See inter
ruption)
configuration 2-2
of storage 3-5
set)
connective
consistency (storage operand)
console device 12-1
control 4-2
control register 2-4,4-8
validity bit 11-23
control-register assignment
bit position y)
13-5,13-17,13-27
4-24,4-27
3-9
5-17
3-23,5-18
6-11
6-12
6-13
6-12
6-12
(PSTL) 3-24
3-24,6-25
3-17,5-18
CR4.16-31:
primary ASN (PASN) 3-13,5-14
5-18,5-21
(SSTL) 3-24