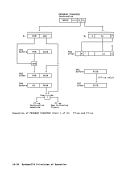
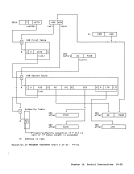
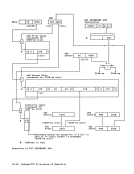
A
A (ADD) binary instruction 7-7
absolute address 3-5
absolute storage 3-5
access-control bits in storage key 3-6
access exceptions 6-28,6-33
priority of 6-33
recognition of 6-28
access key 3-8
for channel-program execution 3-9
for CPU 3-8
access to storage 5-24
(See also reference)
AD (ADDNORMALIZED) instruction 9-6
example A-36
ADD (A,AR) binary instructions 7-7
ADD DECIMAL (AP) instruction 8-5
exampleA-30 ADD HALFWORD (AH) instruction 7-7
example A-8
ADDLOGICAL (AL,ALR) instructions 7-8
ADDNORMALIZED (AD,ADR,AE,AER,AXR)
instructions 9-6
example A-36
ADDUNHORMALIZED (AU,AUR,AW,AWR)
instructions 9-7
example A-36
address 3-2
absolute 3-5
arithmetic 3-6,5-5
unsigned binary 7-3
base (See base address)
branch (See branch address)
channel 13-8,13-15
channel-set 4-43
comparison 12-1
controls for 12-1
effect on CPU state 4-2
CPU (See CPU address)
device 13-8,13-15
effective (See effective address)
failing-storage (See failing-storage
address)
format 3-3
generation 5-5
for storage addressing 3-2I/O (See I/O address)
instruction (See instruction
address)
invalid 6-15
logical (See logical address)
numbering of for byte locations 3-2
PER (See PER address)
prefixing (See prefix)
primary virtual (See primary virtual
address)
real 3-5
secondary virtual (See secondary
virtual address)
storage 3-2
summary information 3-38
translation (See dynamic address
translation, prefix)
types 3-5
virtual 3-5
wraparound (See wraparound)
address space 3-12
control bit
in PSW 4-7
use in address translation 3-22
created byOAT 3-20 number (See ASN)
addressing exception 6-15
as an access exception 6-28,6-33
ADR (ADDNORMALIZED) instruction 9-6
AE (ADDNORMALIZED) instruction 9-6
example A-36
AER (ADDNORMALIZED) instruction 9-6
AFT(ASH first table) 3-14
AFTE (ASN-first-table entry) 3-14AFTO (ASN-first-table origin) 3-13
AFX (ASH-first-table index) 3-13
invalid bit 3-14
translation exception 6-18
AH (ADD HALFWORD) instruction 7-7
example A-8
AKM (authorization key mask) 5-22
AL (ADD LOGICAL) instruction 7-8
alert, I/O-error (in limited channel
logout) 13-82
alert (class of machine-check condition)
11-12
allowed interruptions 6-6
ALR (ADD LOGICAL) instruction 7-8
alter-and-display controls 12-2
alteration
general-register (PER event)4-20 storage (PER event) 4-19 AND (N,NC,NI,NR) instructions 7-8
examples A-8
AP (ADD DECIMAL) instruction 8-5
exampleA-30 AR (ADD) binary instruction 7-7
architectural mode 1-1
compatibility 1-3
arithmetic
address (See address arithmetic)
binary 7-3
examples A-2
decimal 8-2
examples A-5,A-30
floating-point 9-1
examples A-5,A-36
logical (unsigned binary) 7-3
examples A-4
ASCII character code, handled by archi
tecture iv
ASN (address-space number) 3-12
as part of DAS 5-14
authorization 3-17
first table (AFT) 3-14
index (AFX) 3-13
origin(AFTO) 3-13
in entry-table entry 5-22
second table (AST) 3-14
index (ASX) 3-13
origin(ASTO) 3-14
translation 3-13
exceptions 6-35
specification exception 6-18
translation-control bit 3-13,5-18
assembler language A-7
instruction formats in (See instruc
tion lists and page numbers in
Appendix B)
assigned storage locations 3-41
IndexX-I
A (ADD) binary instruction 7-7
absolute address 3-5
absolute storage 3-5
access-control bits in storage key 3-6
access exceptions 6-28,6-33
priority of 6-33
recognition of 6-28
access key 3-8
for channel-program execution 3-9
for CPU 3-8
access to storage 5-24
(See also reference)
AD (ADD
example A-36
ADD (A,AR) binary instructions 7-7
ADD DECIMAL (AP) instruction 8-5
example
example A-8
ADD
ADD
instructions 9-6
example A-36
ADD
instructions 9-7
example A-36
address 3-2
absolute 3-5
arithmetic 3-6,5-5
unsigned binary 7-3
base (See base address)
branch (See branch address)
channel 13-8,13-15
channel-set 4-43
comparison 12-1
controls for 12-1
effect on CPU state 4-2
CPU (See CPU address)
device 13-8,13-15
effective (See effective address)
failing-storage (See failing-storage
address)
format 3-3
generation 5-5
for storage addressing 3-2
instruction (See instruction
address)
invalid 6-15
logical (See logical address)
numbering of for byte locations 3-2
PER (See PER address)
prefixing (See prefix)
primary virtual (See primary virtual
address)
real 3-5
secondary virtual (See secondary
virtual address)
storage 3-2
summary information 3-38
translation (See dynamic address
translation, prefix)
types 3-5
virtual 3-5
wraparound (See wraparound)
address space 3-12
control bit
in PSW 4-7
use in address translation 3-22
created by
addressing exception 6-15
as an access exception 6-28,6-33
ADR (ADD
AE (ADD
example A-36
AER (ADD
AFT
AFTE (ASN-first-table entry) 3-14
AFX (ASH-first-table index) 3-13
invalid bit 3-14
translation exception 6-18
AH (ADD HALFWORD) instruction 7-7
example A-8
AKM (authorization key mask) 5-22
AL (ADD LOGICAL) instruction 7-8
alert, I/O-error (in limited channel
logout) 13-82
alert (class of machine-check condition)
11-12
allowed interruptions 6-6
ALR (ADD LOGICAL) instruction 7-8
alter-and-display controls 12-2
alteration
general-register (PER event)
examples A-8
AP (ADD DECIMAL) instruction 8-5
example
architectural mode 1-1
compatibility 1-3
arithmetic
address (See address arithmetic)
binary 7-3
examples A-2
decimal 8-2
examples A-5,A-30
floating-point 9-1
examples A-5,A-36
logical (unsigned binary) 7-3
examples A-4
ASCII character code, handled by archi
tecture iv
ASN (address-space number) 3-12
as part of DAS 5-14
authorization 3-17
first table (AFT) 3-14
index (AFX) 3-13
origin
in entry-table entry 5-22
second table (AST) 3-14
index (ASX) 3-13
origin
translation 3-13
exceptions 6-35
specification exception 6-18
translation-control bit 3-13,5-18
assembler language A-7
instruction formats in (See instruc
tion lists and page numbers in
Appendix B)
assigned storage locations 3-41
Index