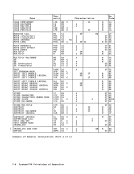
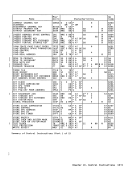
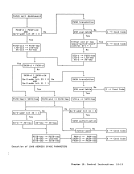
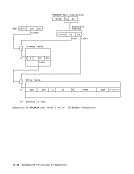
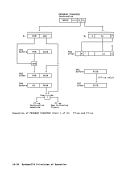
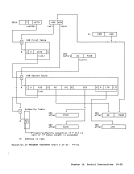
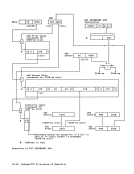
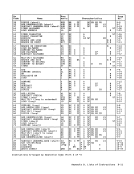
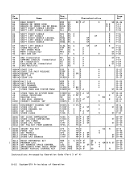
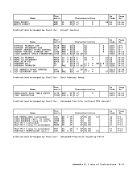
the last and partially in the first
locations of storage and is processed
without anyspecial indication of cross
ing the maximum-address boundary.
Some channels do not perform address
wraparound. Depending on the model, a
program check may be generatedif an
address generated by the channel to
fetch a CCW, to fetchan IDAW, or to
transfer data is incremented past
16,777,215 ordecremented past o. Storage Addressing with Extended Address
Fields
Extended real addressing, 31-bit IDAWs,
theinstructions associated with
storage-key-instruction extensions, and
TESTBLOCK all provide for addresses which are more than 24 bits. This
section describes the handling of these
addresses.
Extended real addressing providesa 26-bit page-frame real address in the
page-table entry for 4K-byte pages.
This address is not subject to wrapa
round because the page-frame real
address designates a 4K-byte block.
Also provided is a 31-bit failing
storage address for certain machine
check interruptions, anda 26-bit
address(extended to 32 bits with zeros
on the left) as a result ofLOAD REAL
ADDRESS.
The 31-bit IDAWs provide a 31-bit abso
lute address of theI/O data area. This
address is not subject to wraparound
because all bytes designated by an IDAW
must lie within a 2K-byte block.
The instructions INSERT STORAGE KEY
EXTENDED, RESET REFERENCE BIT EXTENDED,
SETSTORAGE KEY EXTENDED, and TEST BLOCK specify 31-bit real addresses. These addresses are not subject to wraparound
since they designate a 4K-byte block.INFORMATION FORMATS Information is transmitted between stor
age and aCPU or a channel one byte, or
a group of bytes, at a time.Unless otherwise specified, a group of bytes in
storage is addressed by the leftmost
byte of the group. The number of bytesin the group is either implied or
explicitly specified by the operation to
be performed. When used in aCPU opera
tion,a group of bytes is called a
field.
Within each group of bytes, bits are~ numbered in a left-to-right sequence. ~ The leftmost bits are sometimes referred , to as the "high-order" bits and the
rightmost bits as the "low-order" bits.
Bit numbers are not storage addresses,
however.Only bytes can be addressed.
To operate on individual bits of a byte
in storage, it is necessary to access
theentire byte.
The bitsin a byte are numbered 0 through 7, from left to right.
The bits in an address are numbered 8
through 31 for 24-bit addresses and 1
through 31 for 31-bit addresses. Within
any other fixed-length format of multi
ple bytes, the bits making up the format
are consecutively numbered starting from
o.
For purposes of error detection, and in
some models for correction, one or more
check bits may be transmitted with each
byte or with a group of bytes. Such
check bits are generated automatically
by the machine and cannot bedir€ctly controlled by the program. References
in this publication to the length of
data fields and registers exclude
mention of the associated check bits.
All storage capacities are expressed in
number of bytes.
When the length of a storage-operand
field is implied by the operation code
ofan instruction, the field is said to
havea fixed length, which can be one,
two, four, or eight bytes. Larger
fields may be implied for some
instructions.
When the length of a storage-operand
field is not implied but is stated
explicitly, the field is said to havea variable length. Variable-length oper
ands can vary in length by increments of
one byte.
Wheninformation is placed in storage,
the contents of only those byte
locations are replaced that areincluded in the designated field, even though the width of the physical path to storage
may be greater than the length ofthe field being stored.
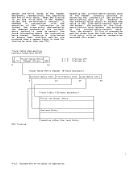
INTEGRALBOUNDARIES Certain units of information must be on
an integral boundary in storage. A
boundary is called integral fora unit
of information when its storage address
is a multiple of the length of the unit
in bytes. Special names are given to
fields of two, four, and eight bytes on
an integral boundary. A halfword is a
group of two consecutive bytes on a
two-byte boundary and is the basic
building block of instructions. A word
isa group of four consecutive bytes on
a four-byte boundary. A doubleword is a
group of eight consecutive bytes on an
eight-byte boundary. (See the figure
Chapter 3. Storage 3-3
locations of storage and is processed
without any
ing the maximum-address boundary.
Some channels do not perform address
wraparound. Depending on the model, a
program check may be generated
address generated by the channel to
fetch a CCW, to fetch
transfer data is incremented past
16,777,215 or
Fields
Extended real addressing, 31-bit IDAWs,
the
storage-key-instruction extensions, and
TEST
section describes the handling of these
addresses.
Extended real addressing provides
page-table entry for 4K-byte pages.
This address is not subject to wrapa
round because the page-frame real
address designates a 4K-byte block.
Also provided is a 31-bit failing
storage address for certain machine
check interruptions, and
address
on the left) as a result of
ADDRESS.
The 31-bit IDAWs provide a 31-bit abso
lute address of the
address is not subject to wraparound
because all bytes designated by an IDAW
must lie within a 2K-byte block.
The instructions INSERT STORAGE KEY
EXTENDED, RESET REFERENCE BIT EXTENDED,
SET
since they designate a 4K-byte block.
age and a
a group of bytes, at a time.
storage is addressed by the leftmost
byte of the group. The number of bytes
explicitly specified by the operation to
be performed. When used in a
tion,
field.
Within each group of bytes, bits are
rightmost bits as the "low-order" bits.
Bit numbers are not storage addresses,
however.
To operate on individual bits of a byte
in storage, it is necessary to access
the
The bits
The bits in an address are numbered 8
through 31 for 24-bit addresses and 1
through 31 for 31-bit addresses. Within
any other fixed-length format of multi
ple bytes, the bits making up the format
are consecutively numbered starting from
o.
For purposes of error detection, and in
some models for correction, one or more
check bits may be transmitted with each
byte or with a group of bytes. Such
check bits are generated automatically
by the machine and cannot be
in this publication to the length of
data fields and registers exclude
mention of the associated check bits.
All storage capacities are expressed in
number of bytes.
When the length of a storage-operand
field is implied by the operation code
of
have
two, four, or eight bytes. Larger
fields may be implied for some
instructions.
When the length of a storage-operand
field is not implied but is stated
explicitly, the field is said to have
ands can vary in length by increments of
one byte.
When
the contents of only those byte
locations are replaced that are
may be greater than the length of
INTEGRAL
an integral boundary in storage. A
boundary is called integral for
of information when its storage address
is a multiple of the length of the unit
in bytes. Special names are given to
fields of two, four, and eight bytes on
an integral boundary. A halfword is a
group of two consecutive bytes on a
two-byte boundary and is the basic
building block of instructions. A word
is
a four-byte boundary. A doubleword is a
group of eight consecutive bytes on an
eight-byte boundary. (See the figure
Chapter 3. Storage 3-3