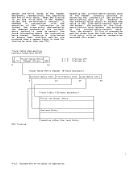
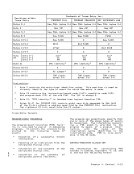
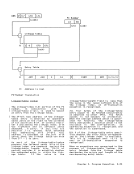
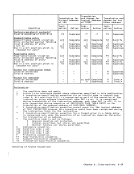
control 10-2 for I/O 13-15 privileged-operation exception 6-23
problem state 4-6
bit inBC-mode PSW 4-8
bit inEC-mode PSW 4-6
bit in entry-table entry 5-22
processing backup (synchronous
machine-check condition) 11-19
processing damage (synchronous
machine-check condition)11-20 processor (See CPU) program
exceptions 6-14
execution of 5-2
initial loading of 4-35
interruption 6-14
forI/O instructions 13-36
imprecise 6-7
priority of6-30 reset 4-34
signal-processor order 4-39PROGRAM CALL (PC) instruction 10-25 trace entry 4-14
program check (channel status)13-70 program-controlled interruption (See PCl)
program-event recording(See PER)
program events(See PER events)
program maskin BC-mode PSW 4-8
inEC-mode PSW 4-7
validity bit for 11-22
program-status word(See PSW) PROGRAM TRANSFER (PT) instruction 10-31 trace entry 4-14
protection (storage) 3-7
during tracing 4-13
fetch(See fetch protection)
key-controlled(See key-controlled
protection)
low-address(See low-address
protection)
segment (See segment protection)
protection check (channel status) 13-71
protection exception 6-23
as an access exception 6-28,6-33
PSTD (primary segment-table designation)
3-24
PSTL (primary segment-table length)
3-24PSTO (primary segment-table origin)
3-24
PSW (program-status word) 2-3,4-3
assigned storage locations for 3-41BC-mode 4-8
current 4-3,5-6
stored during interruption 6-2EC-mode 4-6
exceptions associated with 6-9
format error 6-9
in IPL 4-36
in program execution 5-6
store-status save area for 3-44
validity bits for 11-22
PSW key
inBC-mode PSW 4-8
in EC-modePSW 4-6
used as access key 3-8
validity bit for 11-22
PSW-key-handling facility0-4 PSW-key mask (PKM) 5-18
PT(PROGRAM TRANSFER) instruction 10-31 PT-cp (PROGRAM TRANSFER instruction, to
current primary)10-31 PT-ss (PROGRAM TRANSFER instruction,
with space switching)10-31 PTL (page-table length) 3-25
PTLB (PURGE TLB) instruction10-36 PTO (page-table origin) 3-25
publications, other related documents vPURGE TlB (PTLB) instruction 10-36 PX (page index) 3-21
Q
queuingFIFO, example for lock and unlock
A-44LIFO, example for lock and unlock
A-43
R
start-I/O-fast 13-28
facility0-4 R field of instruction 5-4
range (of floating-point numbers) 9-1
rate control 12-4ROD (READ DIRECT) instruction 10-36 read (1/0 command) 13-49
read backward(I/O command) 13-50 READ DIRECT (RDD) instruction 10-36 read-write-direct facility 4-23
real address 3-5
real mode 3-22
real storage 3-5
receiver check (signal-processor status)
4-42
recovery
as class of machine-check condition
11-12
extension facility0-4 system 11-17
subclass-mask bit for 11-28
redundancy 11-2
reference
bit in storage key 3-6
multiple-access 5-31
recording3-10 sequence for storage 5-24 (See also sequence)
single-access5-30 region code 11-26
assigned storage locations for 3-44
validity bit for 11-22
register
base-address 2-4
control 2-4
designation of 5-4
floating-point 2-4
general 2-4
index 2-4
prefix 3-11
save areas 3-44,11-24
validation of 11-9
validity bits for 11-22
vector-facility 2-4
remote operating stations 12-1
repressible machine-check conditions
11-12
reset4-30 clear 4-34 CPU 4-33
effect onCPU state 4-2
Index X-17
problem state 4-6
bit in
bit in
bit in entry-table entry 5-22
processing backup (synchronous
machine-check condition) 11-19
processing damage (synchronous
machine-check condition)
exceptions 6-14
execution of 5-2
initial loading of 4-35
interruption 6-14
for
imprecise 6-7
priority of
signal-processor order 4-39
program check (channel status)
program-event recording
program events
program mask
in
validity bit for 11-22
program-status word
protection (storage) 3-7
during tracing 4-13
fetch
key-controlled
protection)
low-address
protection)
segment (See segment protection)
protection check (channel status) 13-71
protection exception 6-23
as an access exception 6-28,6-33
PSTD (primary segment-table designation)
3-24
PSTL (primary segment-table length)
3-24
3-24
PSW (program-status word) 2-3,4-3
assigned storage locations for 3-41
current 4-3,5-6
stored during interruption 6-2
exceptions associated with 6-9
format error 6-9
in IPL 4-36
in program execution 5-6
store-status save area for 3-44
validity bits for 11-22
PSW key
in
in EC-mode
used as access key 3-8
validity bit for 11-22
PSW-key-handling facility
PT
current primary)
with space switching)
PTLB (PURGE TLB) instruction
publications, other related documents v
Q
queuing
A-44
A-43
R
start-I/O-fast 13-28
facility
range (of floating-point numbers) 9-1
rate control 12-4
read backward
real address 3-5
real mode 3-22
real storage 3-5
receiver check (signal-processor status)
4-42
recovery
as class of machine-check condition
11-12
extension facility
subclass-mask bit for 11-28
redundancy 11-2
reference
bit in storage key 3-6
multiple-access 5-31
recording
single-access
assigned storage locations for 3-44
validity bit for 11-22
register
base-address 2-4
control 2-4
designation of 5-4
floating-point 2-4
general 2-4
index 2-4
prefix 3-11
save areas 3-44,11-24
validation of 11-9
validity bits for 11-22
vector-facility 2-4
remote operating stations 12-1
repressible machine-check conditions
11-12
reset
effect on
Index X-17