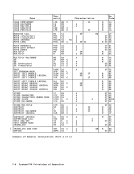
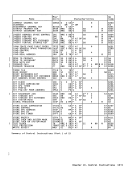
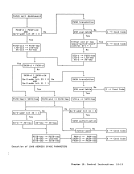
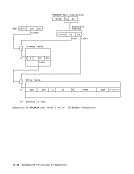
Programming Note The independent fetching of a single
location for each of two operands may
affect the program execution in the
following situation.
When the same storage locationis desig nated by two operand addresses of an
instruction, and another CPU or a chan
nel causes the contents of the location
to change during execution of the
instruction, the oldand new values of the location may be used simultaneously.
Forexample, comparison of a field to
itself may yielda result other than
equal, orEXCLUSIVE-ORing of a field
with itselfmay yield a result other than zero. OTHER STORAGE REFERENCES The resta rt, program, superv i so r-ca 11, external, input/output, and mach; ne check PSWs appear to be accessed doubleword-concurrent as observed by other CPUs. Those references appear to
occur after the conceptually previousunit of operation and before the concep
tually subsequent unit of operation.The relationship between the new-PSW fetch, the old-PSW store, and the
interruption-code store is unpredic
table.Store accesses for interruption codes
not stored within the oldPSW are not
necessarily single-access stores. The
store accesses for the external and
supervisor-calI-interruption codes
appear to occurbetween the conceptually
previousand conceptually subsequent
operations.The store accesses for the program-interruption codes may precede the storage-operand references associ
ated with the instruction which results
in the program interruption.
The stores into theCSW and 1/0- communication area occur within the
conceptual limits of the interruption orI/O instruction with which they are associated.
Updating ofthe interval timer occurs
after storage-operand references for the
conceptuallyprevl0us instruction and before storage-operand references for the conceptually subsequent instruction.
Interval-timerupdates can also occur
within an interruptible instructionbetween units of operation. SERIALIZATION Th2 sequence of functions performed by a CPU is normally independent of the func-
tions performed by other CPUs and by
channels.Similarly, the sequence of
functions performed by a channelis normally independent of the functions
performed by other channels and byCPUs. However, at certain points in its
execution, serialization of theCPU occurs. Serialization also occurs at
certain points for channel programs.
CPUSERIALIZATION All interruptions and the execution of
certain instructions cause a serializa
tion of CPU operations. A serialization
operation consists in completing all
conceptually previous storage accesses
by theCPU, as observed by other CPUs and by channels, before the conceptually
subsequent storage accesses occur.Serialization affects the sequence of
allCPU accesses to storage and to the
storage keys, except for those associ
ated with DAT-table-entry fetching.Serialization is performed by CPU reset,
all interruptions, and by the execution
of the following instructions!• The general instructions BRANCH ON CONDITION (BCR) with the M t and R2 field containing all ones and all
zeros, respectively, andCOMPARE AND SWAP, COMPARE DOUBLE AND SWAP, STORE CLOCK, SUPERVISOR CALL, and
TEST ANDSET. • • • • • LOAD PSW, SET STORAGE KEY, and SET STORAGE KEY EXTENDED.
AllI/O instructions, CONNECT CHAN
NELSET, and DISCONNECT CHANNEL SET. PURGE TLB and SET PREFIX, which
also cause the translation
lookaside buffer tobe cleared of
entries.SIGNAL PROCESSOR, READ DIRECT, and L,JR IT E D IRE CT.
INVALIDATEPAGE TABLE ENTRY. • TEST BLOCK. • • MOVE TO PRIMARY, MOVE TO SECONDARY, PROGRAM CALL, PROGRAM TRANSFER, SET
ADDRESSSPACE CONTROL, and SET SECot~DARY ASN. The DAS-tracing function causes
serialization to beperformed before the trace action and after
completion ofthe trace action. The sequence of events associated with a
serializing operation is as follows:
1. All conceptually previous storage
accesses by theCPU are completed
Chapter 5.Program Execution 5-33
location for each of two operands may
affect the program execution in the
following situation.
When the same storage location
instruction, and another CPU or a chan
nel causes the contents of the location
to change during execution of the
instruction, the old
For
itself may yield
equal, or
with itself
occur after the conceptually previous
tually subsequent unit of operation.
interruption-code store is unpredic
table.
not stored within the old
necessarily single-access stores. The
store accesses for the external and
supervisor-calI-interruption codes
appear to occur
previous
operations.
ated with the instruction which results
in the program interruption.
The stores into the
conceptual limits of the interruption or
Updating of
after storage-operand references for the
conceptually
Interval-timer
within an interruptible instruction
tions performed by other CPUs and by
channels.
functions performed by a channel
performed by other channels and by
execution, serialization of the
certain points for channel programs.
CPU
certain instructions cause a serializa
tion of CPU operations. A serialization
operation consists in completing all
conceptually previous storage accesses
by the
subsequent storage accesses occur.
all
storage keys, except for those associ
ated with DAT-table-entry fetching.
all interruptions, and by the execution
of the following instructions!
zeros, respectively, and
TEST AND
All
NEL
also cause the translation
lookaside buffer to
entries.
INVALIDATE
ADDRESS
serialization to be
completion of
serializing operation is as follows:
1. All conceptually previous storage
accesses by the
Chapter 5.