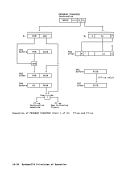
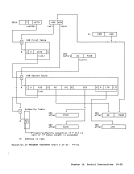
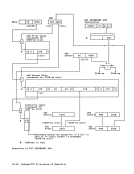
byte-multiplexer channel 13-4,13-30 byte-oriented-operand facility 3-5
C
C(COMPARE) binary instruction 7-12
cache 3-2
CAr (channel-available interruption)
13-29,13-61
carry 7-3
CAW (channel-address word) 13-37
assigned storage locations for 3-42
inIPl 4-36
CBC (checking-block code) 11-2
invalid 11-2
in registers 11-9
in storage 11-6
in storage keys 11-7
near-valid 11-2
valid 11-2
CC (chain-command) flag in CCW
13-7,13-38
CCW (channel-command word) 13-38
address of in CAW 13-37
address of inCSW 13-63
contents of 13-75
validity flag for 13-82
chaining of13-40 commands (See command chaining of
cews)
data (See data chaining of CCWs)
command codes (See commands)
command retry of 13-53
count field in (See count field)
data-address field in 13-39
flags in 13-49
format of 13-38
inrPl 4-36
assigned storage locations for
3-41
prefetching of13-40,13-42 role of in I/O operations 13-5
CD (chain-data) flag in CCW 13-6,13-38
CD(COMPARE) floating-point instruction
9-8
CDR(COMPARE) floating-point instruction
9-8
examples A-37
CDS(COMPARE DOUBLE AND SWAP) instruc
tion 7-12
examplesA-40 CE (COMPARE) floating-point instruction
9-8
central processing unit (SeeCPU) CER (COMPARE) floating-point instruction
9-8
CH(COMPARE HAlFWORD) instruction 7-14
example A-12
chain-command (CC) flag in CCW
13-7,13-38
chain-data (CD) flag in cew 13-6,13-38
chaining13-40 command (See command chaining of
CCWs)
data (See data chaining of CCWs)
flags in CCW for 13-6,13-38
chaining check (channel status) 13-72
change bit in storage key 3-7
change recording3-10 channel 2-6,13-3
block-multiplexer 13-5
byte-multiplexer13-4,13-30 control failure (bit in
external-damage code) 11-25
equipment error detected by 13-14
I/O-system reset, as part of subsys
tem reset 4-34
masks 6-14
difference between EC and BC modes
4-4
in BC-modePSW 4-8
multiplexer 13-5
not operational (I/O-system state)
13-12
bit in external-damage code 11-25
programming error dptected by 13-14
selector 13-4
timeout used by 13-4
working (I/O-system state) 13-11
channel address 13-8,13-15
channel-address word (See CAW)
channel-available interruption (CAl)
13-29,13-61
channel-command word (See CeW)
channel commands (See commands)
channel-control check (channel status)
13-72
channel-data check (channel status)
13-71
channel end (unit status) 13-67
channel identification (rD) 13-32
assigned storage locations for 3-44
inIOeA (I/O-communication area) 13-80 channel indirect data addressing 13-45
facility D-2
IDA flag used for 13-38
role of inI/O operations 13-6
channel logout (See full channel
logout)
(See also limited channel logout)
channel model 13-32
channel power-on reset 4-35
channel program 13-5
resumption of 13-55
serialization 5-34
suspension of 13-46
channel set 2-6
address 4-43
resetting of connections for 4-34
switching 4-43
switching facility D-2
channel status13-70 chaining check 13-72
channel-control check 13-72
channel-data check 13-71
incorrect length13-70 interface-control check 13-72
program check13-70 program-controlled interruption (PCI) 13-70 protection check 13-71
channel-status word (See CSW)
channel-to-channel adapter 13-2
publication referenced v
channel-type code (specified by STIDC)
13-32
characteristic (of floating-point
number) 9-1
characters, represented by eight-bit
code iv
check bits 3-3,11-2
check stop4-3,11-10 as signal-processor status 4-42
control bit 11-14,11-28
during manual operation 12-1
Index X-3
C
C
cache 3-2
CAr (channel-available interruption)
13-29,13-61
carry 7-3
CAW (channel-address word) 13-37
assigned storage locations for 3-42
in
CBC (checking-block code) 11-2
invalid 11-2
in registers 11-9
in storage 11-6
in storage keys 11-7
near-valid 11-2
valid 11-2
CC (chain-command) flag in CCW
13-7,13-38
CCW (channel-command word) 13-38
address of in CAW 13-37
address of in
contents of 13-75
validity flag for 13-82
chaining of
cews)
data (See data chaining of CCWs)
command codes (See commands)
command retry of 13-53
count field in (See count field)
data-address field in 13-39
flags in 13-49
format of 13-38
in
assigned storage locations for
3-41
prefetching of
CD (chain-data) flag in CCW 13-6,13-38
CD
9-8
CDR
9-8
examples A-37
CDS
tion 7-12
examples
9-8
central processing unit (See
9-8
CH
example A-12
chain-command (CC) flag in CCW
13-7,13-38
chain-data (CD) flag in cew 13-6,13-38
chaining
CCWs)
data (See data chaining of CCWs)
flags in CCW for 13-6,13-38
chaining check (channel status) 13-72
change bit in storage key 3-7
change recording
block-multiplexer 13-5
byte-multiplexer
external-damage code) 11-25
equipment error detected by 13-14
I/O-system reset, as part of subsys
tem reset 4-34
masks 6-14
difference between EC and BC modes
4-4
in BC-mode
multiplexer 13-5
not operational (I/O-system state)
13-12
bit in external-damage code 11-25
programming error dptected by 13-14
selector 13-4
timeout used by 13-4
working (I/O-system state) 13-11
channel address 13-8,13-15
channel-address word (See CAW)
channel-available interruption (CAl)
13-29,13-61
channel-command word (See CeW)
channel commands (See commands)
channel-control check (channel status)
13-72
channel-data check (channel status)
13-71
channel end (unit status) 13-67
channel identification (rD) 13-32
assigned storage locations for 3-44
in
facility D-2
IDA flag used for 13-38
role of in
channel logout (See full channel
logout)
(See also limited channel logout)
channel model 13-32
channel power-on reset 4-35
channel program 13-5
resumption of 13-55
serialization 5-34
suspension of 13-46
channel set 2-6
address 4-43
resetting of connections for 4-34
switching 4-43
switching facility D-2
channel status
channel-control check 13-72
channel-data check 13-71
incorrect length
program check
channel-status word (See CSW)
channel-to-channel adapter 13-2
publication referenced v
channel-type code (specified by STIDC)
13-32
characteristic (of floating-point
number) 9-1
characters, represented by eight-bit
code iv
check bits 3-3,11-2
check stop
control bit 11-14,11-28
during manual operation 12-1
Index X-3