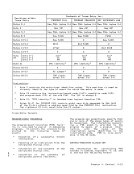
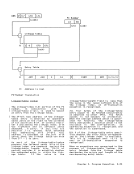
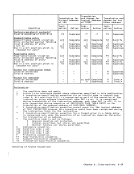
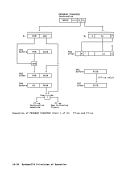
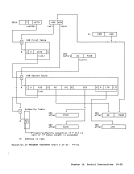
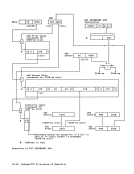
D
D (DIVIDE) binary instruction 7-17example A-16
D field of instruction 5-5damage code (external) 11-24
validity bit for 11-22external 11-18
mask bit for 11-28
instruction-processing 11-17
interval-timer 11-17
processing 11-20
service-processor 11-18
system 11-16
timing-facility 11-17
DAS (dual-address-space) facility
D-2,5-13
authorization mechanisms 5-17
summary of5-20 tracing (See tracing)
DAT(See dynamic address translation)
DAT mode (bit in PSW) 4-6use in address translation 3-22
data
format for
decimal instructions 8-1
floating-point instructions 9-2general instructions 7-2 I/O-sense 13-51
prefetching of for output operation13-40 transfer (I/O), conclusion of 13-56
data block(See block of I/O data)
data chaining ofCCWs 13-6,13-42
as cause of chaining check 13-72CCW prefetch for 13-42
chain-data(CD) flag in CCW 13-6,13-38
effect on compatibility of 13-8
data check (bit inI/O-sense data)
13-51
data exception 6-18
DD (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
DDR (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
DE (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
decimal
arithmetic 8-2
comparison 8-5
digit codes 8-2
divide exception 6-19
instructions 8-1examples A-30 number representation 8-1 examples A-5
operand overlap 8-3
overflow
exception 6-19
mask inBC-mode PSW 4-8
mask inEC-mode PSW 4-7
sign codes 8-2
tables for conversion to hexadecimal
F-1
decimal-to-binary conversion 7-16
example A-16
deferred condition code (inCSW) 13-63
contents of 13-74
forSIOF function 13-29
degradation (machine-check condition)
11-18
subclass-mask bit for 11-28
degradation, storage (machine-check
condition) 11-21
delay code in I/O-communication area
13-83
delay in storing 5-29
delayed (machine-check condition) 11-19
delayed access exception (machine-check
condition) 11-19
deletion of malfunctioning unit 11-4
DER (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
examples A-37
designation
authority-table 3-14
effective segment-table 3-27
entry-table 5-21
linkage-table 5-21
in AST entry 3-15
page-table 3-25
primary segment-table 3-24
secondary segment-table 3-24
segment-table 3-24
in AST entry 3-14
destructive overlap 5-32,7-25
detect field (in limited channel logout)
13-81device 2-6,13-2
console 12-1
not-ready state of13-10 status of 13-51
used for IPL 4-36
device address 13-8,13-15device busy (unit status) 13-29
deviceend (unit status) 13-29,13-67
device error 13-15
device-working state (I/O-system state)13-10 DIAGNOSE instruction 10-5 digit codes (decimal) 8-2
digit selector (in EDIT) 8-7
direct-access storage 3-2
direct control 4-23
facility D-2
disabling for interruptions 6-6
disabling of interval timer 4-29
disallowed interruptions 6-6DISCONNECT CHANNEL SET (DISCS) instruc-
tion10-6 DISCS (DISCONNECT CHANNEL SET) instruc
tion10-6 displacement (in relative addressing)
5-5
display (manual controls) 12-2
DIVIDE (D,DR) binary instructions 7-17
example A-16
DIVIDE (DD,DDR,DE,DER) floating-point
instructions 9-9
examples A-37
DIVIDEDECIMAL (DP) instruction 8-5
example A-31
divide exception
decimal 6-19
fixed-point6-20 floating-point 6-20 divisible instruction execution 5-25
doubleword 3-3
doubleword-concurrent storage references
5-31
DP (DIVIDEDECIMAL) instruction 8-5
example A-31
DR (DIVIDE) binary instruction 7-17
dual-address-space facility (See DAS)
dump (standalone) 12-5
dynamic address translation (DAT)3-20 Index X-7
D (DIVIDE) binary instruction 7-17
D field of instruction 5-5
validity bit for 11-22
mask bit for 11-28
instruction-processing 11-17
interval-timer 11-17
processing 11-20
service-processor 11-18
system 11-16
timing-facility 11-17
DAS (dual-address-space) facility
D-2,5-13
authorization mechanisms 5-17
summary of
DAT
DAT mode (bit in PSW) 4-6
data
format for
decimal instructions 8-1
floating-point instructions 9-2
prefetching of for output operation
data block
data chaining of
as cause of chaining check 13-72
chain-data
effect on compatibility of 13-8
data check (bit in
13-51
data exception 6-18
DD (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
DDR (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
DE (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
decimal
arithmetic 8-2
comparison 8-5
digit codes 8-2
divide exception 6-19
instructions 8-1
operand overlap 8-3
overflow
exception 6-19
mask in
mask in
sign codes 8-2
tables for conversion to hexadecimal
F-1
decimal-to-binary conversion 7-16
example A-16
deferred condition code (in
contents of 13-74
for
degradation (machine-check condition)
11-18
subclass-mask bit for 11-28
degradation, storage (machine-check
condition) 11-21
delay code in I/O-communication area
13-83
delay in storing 5-29
delayed (machine-check condition) 11-19
delayed access exception (machine-check
condition) 11-19
deletion of malfunctioning unit 11-4
DER (DIVIDE) floating-point instruction
9-9
examples A-37
designation
authority-table 3-14
effective segment-table 3-27
entry-table 5-21
linkage-table 5-21
in AST entry 3-15
page-table 3-25
primary segment-table 3-24
secondary segment-table 3-24
segment-table 3-24
in AST entry 3-14
destructive overlap 5-32,7-25
detect field (in limited channel logout)
13-81
console 12-1
not-ready state of
used for IPL 4-36
device address 13-8,13-15
device
device error 13-15
device-working state (I/O-system state)
digit selector (in EDIT) 8-7
direct-access storage 3-2
direct control 4-23
facility D-2
disabling for interruptions 6-6
disabling of interval timer 4-29
disallowed interruptions 6-6
tion
tion
5-5
display (manual controls) 12-2
DIVIDE (D,DR) binary instructions 7-17
example A-16
DIVIDE (DD,DDR,DE,DER) floating-point
instructions 9-9
examples A-37
DIVIDE
example A-31
divide exception
decimal 6-19
fixed-point
doubleword 3-3
doubleword-concurrent storage references
5-31
DP (DIVIDE
example A-31
DR (DIVIDE) binary instruction 7-17
dual-address-space facility (See DAS)
dump (standalone) 12-5
dynamic address translation (DAT)