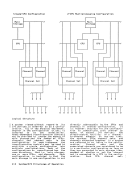
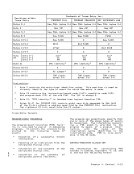
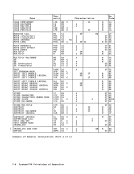
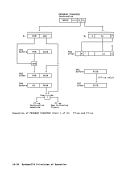
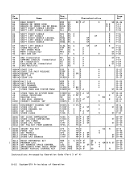
Function Performed on
1CPU on Which Key
Key Activated Was Activated
System-reset-normal
key• without store-Initial CPU reset
status facility• with store- CPU reset
status facilityOther CPUs in Config CPU reset
Remainder ofConfiguration Subsystem reset
Subsystem reset
System-reset-clearClear reset
2
keyClear reset
2Clear reset
J
Load-normal key InitialCPU reset, CPU reset
followed byIPL Subsystem reset
Load-clear keyClear reset
2
,
followed byIPL Clear reset
2Clear reset
J
Explanation:* This situation cannot occur, since the store-status facility is
provided in aCPU equipped for multiprocessing.
1 Activation of a system-reset or load key may change the config
uration, including the connection withI/O, storage units, and
otherCPUs. 2 Only the CPU elements of this reset apply. J Only the non-CPU elements of this reset apply.
Manual Initiation of ResetsChapter 4. Control 4-31
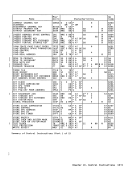
1
Key Activated Was Activated
System-reset-normal
key
status facility
status facility
Remainder of
Subsystem reset
System-reset-clear
2
key
2
J
Load-normal key Initial
followed by
Load-clear key
2
,
followed by
2
J
Explanation:
provided in a
1 Activation of a system-reset or load key may change the config
uration, including the connection with
other
Manual Initiation of Resets