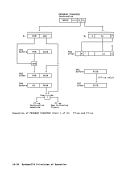
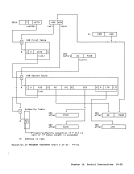
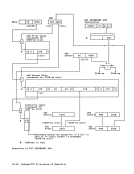
length (LTL) 5-21
origin(LTO) 5-21
LM(LOAD MULTIPLE) instruction 7-22
LNDR(LOAD NEGATIVE) floating-point
instruction 9-11
LNER(LOAD NEGATIVE) floating-point
instruction 9-11
LNR(LOAD NEGATIVE) binary instruction
7-22LOAD (L,LR) binary instructions 7-20 example A-20 LOAD (LD,LDR,LE,LER) floating-point
instructions9-10 LOAD ADDRESS (LA) instruction 7-21
examplesA-20 LOAD ADDRESS SPACE PARAMETERS (LASP) instruction 10-12 LOAD AND TEST (LTDR,LTER) floating-point
instructions 9-11LOAD AND TEST (LTR) binary instruction
7-21
load-clear keyLOAD COMPLEMENT floating-point LOAD COMPLEMENT 7-21
12-3
(LCDR,LCER)
instructions 9-11
(LCR) binary instructionLOAD CONTROL (LCTL) instruction 10-20 LOAD HALFWORD (LH) instruction 7-22
examplesA-20 load indicator 12-3 LOAD MULTIPLE (LM) instruction 7-22 LOAD NEGATIVE (LNDR,LNER) floating-point
instructions 9-11LOAD NEGATIVE (LNR) binary instruction
7-22
load-normal key 12-3LOAD POSITIVE (LPDR,LPER) floating-point
instructions 9-12LOAD POSITIVE (LPR) binary instruction
7-22LOAD PSW (LPSW) instruction 10-20 LOAD REAL ADDRESS (LRA) instruction 10-21 LOAD ROUNDED (LRDR,LRER) instructions
9-12
load state 4-2,4-3
duringIPL 4-35
load-unit-address controls 12-3
loading, initial (See IML,IPL) location 3-2 (See also address)
not available in configuration 6-15
location80 (for interval timer) 4-29
location 84 (in tracing) 4-13
lock A-42
example withFIFO queuing A-45
example withLIFO queuing A-44
logical
arithmetic (unsigned binary) 7-3
comparison 7-4
connectiveAND 7-8
EXCLUSIVEOR 7-18 OR 7-30 data 7-2
logical address 3-6
handling by DAT 3-22
logout
channel13-80 extended machine-check 11-28
address 11-29
length of 11-23
validity bit for 11-23
fixed
assigned storage locations for
3-44
channel(See full channel logout)
machine-check 11-28I/O extended (See IOEL) limited channel (See limited channel
logout)
logout pending (bit in CSW) 13-63
long floating-point number 9-2
longI/O block 13-70 loop control 5-6
loop of interruptions(See string of
interruptions)
low-address protection 3-9
control bit 3-9
exception for 6-23LPDR (LOAD POSITIVE) floating-point
instruction 9-12LPER (LOAD POSITIVE) floating-point
instruction 9-12LPR (LOAD POSITIVE) binary instruction
7-22LPSW (LOAD PSW) instruction 10-20 LR (LOAD) binary instruction 7-20 LRA (LOAD REAL ADDRESS) instruction 10-21 LRDR (LOAD ROUNDED) instruction 9-12
LRER(LOAD ROUNDED) instruction 9-12
LT (linkage table) 5-21
LTD (linkage-table designation) 5-21
LTDR(LOAD AND TEST) floating-point
instruction 9-11
LTER(LOAD AND TEST) floating-point
instruction 9-11
LTL (linkage-table length) 5-21LTO (linkage-table origin) 5-21
LTR(LOAD AND TEST) binary instruction
7-21
LX (linkage index) 5-21
invalid bit 5-21
translation exception6-20 M
M (mega) iv
M(MULTIPLY) binary instruction 7-28
example A-24
machine check 11-2(See also malfunction)
extended logout (MCEL) 11-28
address 11-29
length of 11-23
validity bit for 11-23
handling of malfunction detected as
part ofI/O 11-5
interruption 6-14,11-11
action 11-12
code (MCIC) 3-44,11-15
floating conditions 11-27
mask in BC-modePSW 4-8
mask in EC-modePSW 4-6
subclass masks in control register
11-27
logout 11-28
control bits for 11-29
mask, in EC-modePSW 4-6
mask in BC-modePSW 4-8
main storage 3-2(See also storage) effect of power-on reset on 4-35
shared (in multiprocessing) 4-38
malfunction 11-2
correction of 11-2
Index X-13
origin
LM
LNDR
instruction 9-11
LNER
instruction 9-11
LNR
7-22
instructions
examples
instructions 9-11
7-21
load-clear key
12-3
(LCDR,LCER)
instructions 9-11
(LCR) binary instruction
examples
instructions 9-11
7-22
load-normal key 12-3
instructions 9-12
7-22
9-12
load state 4-2,4-3
during
load-unit-address controls 12-3
loading, initial (See IML,
not available in configuration 6-15
location
location 84 (in tracing) 4-13
lock A-42
example with
example with
logical
arithmetic (unsigned binary) 7-3
comparison 7-4
connective
EXCLUSIVE
logical address 3-6
handling by DAT 3-22
logout
channel
address 11-29
length of 11-23
validity bit for 11-23
fixed
assigned storage locations for
3-44
channel
machine-check 11-28
logout)
logout pending (bit in CSW) 13-63
long floating-point number 9-2
long
loop of interruptions
interruptions)
low-address protection 3-9
control bit 3-9
exception for 6-23
instruction 9-12
instruction 9-12
7-22
LRER
LT (linkage table) 5-21
LTD (linkage-table designation) 5-21
LTDR
instruction 9-11
LTER
instruction 9-11
LTL (linkage-table length) 5-21
LTR
7-21
LX (linkage index) 5-21
invalid bit 5-21
translation exception
M (mega) iv
M
example A-24
machine check 11-2
extended logout (MCEL) 11-28
address 11-29
length of 11-23
validity bit for 11-23
handling of malfunction detected as
part of
interruption 6-14,11-11
action 11-12
code (MCIC) 3-44,11-15
floating conditions 11-27
mask in BC-mode
mask in EC-mode
subclass masks in control register
11-27
logout 11-28
control bits for 11-29
mask, in EC-mode
mask in BC-mode
main storage 3-2
shared (in multiprocessing) 4-38
malfunction 11-2
correction of 11-2
Index X-13