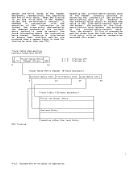
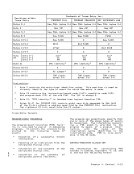
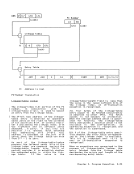
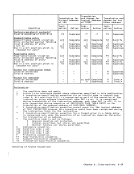
access exceptions for
signal-processor order for 4-39
instruction
instruction
caused by clock comparator 4-27
caused by
9-15
subchannel 13-4
not operational
13-11
working
subchannel
in
contents of 13-73
validity flag for 13-82
used as access
used for
subclass-mask bits 6-6
external-interruption
subroutine linkage 5-6
subsystem-linkage-control bit 5-18,5-21
subsystem reset 4-34
7-36
7-37
instructions 9-14
successful-branching
mask for 4-16
supervisor-call interruption 6-36
supervisor state 4-6
suppress-Iength-indication (SLI) flag in
suppression
exceptions to 5-11
of instruction execution 5-9
of unit of operation
9-15
suspend-and-resume facility D-5,13-7
suspended (bit in
suspension of channel-program execution
13-28,13-46
suspend (S) flag in
suspend-control bit in
meaning of 13-74
9-15
swapping
by
by
switching of channel sets 4-43
SWR
9-15
SX (segment index) 3-21
SXR
9-14
synchronization
checkpoint 11-3
of
of
synchronous logout 11-28
synchronous machine-check
extended-Iogout-control bit 11-29
synchronous machine-cheek-interruption
conditions 11-19
system
manual control of 12-1
organization of 2-1
system check stop 11-11
system damage 11-16
system mask (in
validity bit for 11-22
system recovery 11-17
system reset
system-reset-normal
T
table of powers of 2 E-l
tables
ASN (See ASN first table, ASN second
table)
authority
DAT (See page table, segment table)
entry
hexadecimal F-1
linkage
page (See page table)
segment
translation 3-25
target instruction 7-19
TB (TEST
termination
of
ations)
by channel or
by
by
by HALT
13-59
of instruction execution 5-9
for
tions 11-11
of unit of operation
tions 11-11
termination code (in limited channel
logout) 13-82
Index X-21